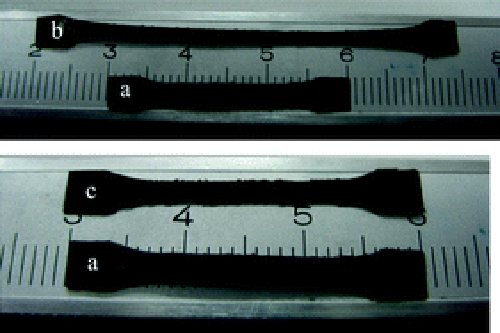
AzoPU (sample A) showing shape memory effect at 75℃: (a) initial state; (b) deformed state (stretched at 75℃ and fixed at 25℃); (c) recovered state after heating in oven at 75℃. (WANG Qihua et al.)
Researchers at the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (LICP, CAS) have made progress in Shape Memory Polyurethanes (SMPU) by introducing azo into the polyurethanes main chains.
Composed of reversible phase and fixed phase, SMPU can be tailored to exhibit multi-functions by introducing special functionalized soft segment and hard segment into the polymers. It presents promising application in bionic and biomedical fields due to its biocompatibility, biodegradation, and tunable transition temperature.
Researchers of LICP synthesized and characterized SMPU with azo as hard segments in their study. They found that the azobenzene-containing polyurethanes exhibited not only excellent shape memory effect but also photoisomerization function, which may be helpful in expanding the application of SMPU in areas of drug release and optical data storage.
The research has received support from the Innovative Group Foundation from Nation Natural Science Foundation of China, Main Direction Program of Knowledge Innovation of CAS and National Program on Key Basic Research Project of China (973 Program).
The main findings have been published in J. Mater. Chem. (2010, 20, 9976–9981).
Further reference:
Journal of Materials Chemistry paper
Page of WANG Qihua (corresponding author of the paper)
