Ion implantation is an effective technique in modifying the surface property, structure and morphology of materials, with no limitation on the variety of the materials.
Researchers at the State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication of the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP), CAS, have recently achieved the surface amorphization and deoxygenation of graphene oxide (GO) paper using Ti ion implantation, which opens up a new strategy for the surface modification of GO materials. It can also improve the optical, magnetic, and electrical properties of GO materials as well as expand the applications of GO-based nanodevices.
Previously, the researchers have successfully prepared the graphene/amorphous carbon composites films (Carbon (2010), 48, 2644-2673).
Their work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China . The findings have been published in Carbon (Carbon (2011), 49, 3141-3147).
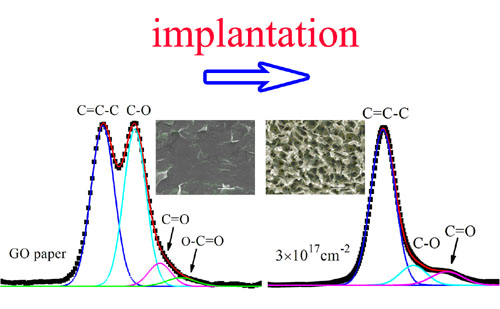
The surface chemical states and morphologies of the GO paper before and after Ti ion implantation. (Image by YAN Xingbin et al.)
CarbonPaper (Carbon(2010), 49, 3141-3147)
Carbon Paper(Carbon(2010), 48, 2644-2673)
Prof. YAN Xingbin's homepage
