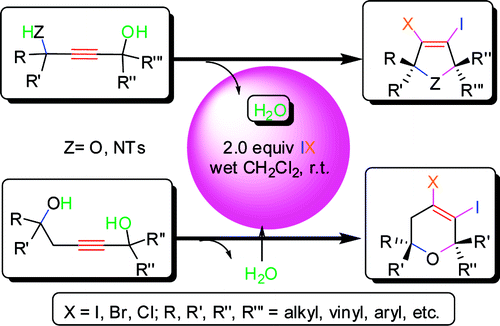
Researchers of the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics prepared highly substituted dihalogenated dihydrofurans, dihydropyrroles, and dihydro-2H-pyrans bearing alkyl, vinyl, aryl, and heteroaryl moieties in good to excellent yields (up to 99%) by allowing 1,4-butyne-diol, 4-aminobut-2-yn-1-ol, and pent-2-yne-1,5-diol derivatives to react with different electrophiles (I2, IBr, and ICl) at room temperature. This method tolerates many alkyl, vinyl, aryl, and heteroaryl functional groups.
Both halogen atoms generated from electrophiles were used effectively. The dihalogenated moiety can be readily introduced into the heterocycle in a position not easily obtained previously. Subsequent functionalization of the resulting heterocycles by palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions leads to a number of interesting five- and six-membered substituted skeletons. In addition, the presence of a trace amount of water is needed for this electrophilic cyclization.
In past decades, the synthesis of heterocycles has continued to attract the interest of synthetic chemists due to the number of these compounds that show antidepressant, antihypertensive, and hypoglycemic activities as well as other biological effects.1 Among these heterocycles, the five- and six-membered oxygenated or nitrogenated heterocycles are probably one of the most common structural subunits in numerous natural products.Thus, a mild, metal-free, environmentally benign and atom economic protocol for the straightforward annulation of five- and six-membered heterocyclic rings is still of high demand.
The work has received support from the NSF and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. The findings have been published in J. Org. Chem. (J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 5670–5678).
J. Org. Chem.Paper
