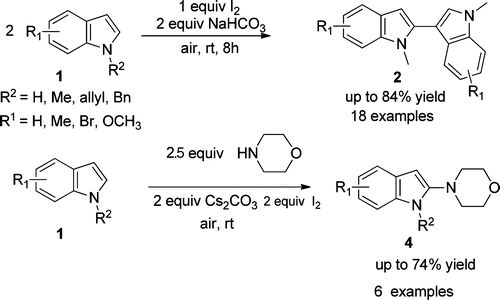
A mild, metal-free, and environmentally benign iodine-promoted regioselective C-C and C-N bonds formation of N-protected indole derivatives giving 2,30-biindoles 2 and 4-(1H-indol-2-yl)morpholines 4 is successfully demonstrated by researchers of Lanzhou University and Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP) of the CAS. The key step of the process is the attack of indoles or morpholine on 3-iodo-3H-indol-1-iumsBtriggered by iodonium at room temperature. Various bioactive 2,30-biindoles and 4-(1Hindol-2-yl)morpholines, bearing electron-rich to moderately electron-poor substituents, can be prepared in moderate to good yields.
Synthesis of 2,30-biindolyl7a-d and 4-(1H-indol-2-yl)morpholine scaffolds,7e which are useful structural units that are frequently found in pharmaceuticals and functional materials, look quite attractive. Both chemical and enzymatic synthetic methods have been reported for the construction of biindolyls. However, most of the procedures require expensive metal catalysts and high loading of metal oxidants and more attention has been paid to the direct C-C bond formation of indoles. Moreover, examples of the direct functionalization of indoles with selective C-N bond formation are rarely reported. Therefore, a new and effective practical reaction system, involving mild, environmently benign, atom economic, and metal-free conditions, for the regioselective construction of C-C and C-N bonds of N-protected indole derivatives is still of high demand in modern organic synthesis.
In recent years, the electrophile-promoted tandem reactions have proven to be an effective method for the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds. The researchers and others have reported that the electrophilic cyclization can be a very powerful tool for the preparation of a wide variety of interesting heterocyclic compounds, due to the efficient, mild, and clean reactions. Thus, electrophile-promoted tandemreactions continue to be an area of active research in the field of synthetic chemistry.
The work has received support from the National Science Foundation of China. The detailed report has been published in J. Org. Chem.( J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 744–747).
J. Org. Chem.Paper
