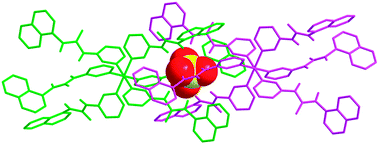
A sulfate capsule formed by copper(II) sulfate and a naphthyl-decorated mono-pyridylurea ligand have been developed by researchers from the Northwest University and Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics of the CAS. In complex complex [CuL6]·3[CuL2(DMF)4](SO4)4, two C3-clefts of the octahedral complexes create a cavity that encapsulates the sulfate anion by six urea groups.
Anion complexation by synthetic receptors is a widely cultivated area in supramolecular chemistry. Due to the biological and environmental importance of the sulfate ion, the design of efficient sulfate-selective receptors has attracted much attention. However, the binding and separation of sulfate is highly challenging because of its high charge density and hydration energy according to the Hofmeister effect. A promising approach for sulfate separation is completely encapsulating the anion. To this end, many organic ligands possessing good complementarity for the tetrahedral sulfate ion have already designed by the researchers.
On the other hand, sulfate capsules can also be constructed with the aid of metal coordination. Metal complexes allow for the pre-orientation of the building blocks according to the metal coordination geometry to offer a complementary binding environment for anions. Moreover, some metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) functionalized with flexible bis-pyridylurea ligands have also been reported to encapsulate sulfate ion by four urea groups.
The pyridylurea ligands have proven to be excellent candidates for metal-based anion receptors. In principle, the coordination of six mono-pyridylurea ligands around an octahedral metal ion should result in two C3 clefts at the ends of the molecule, and two molecules may interdigitate along the C3-axis to afford a cavity with six urea groups for effective sulfate binding. Unfortunately, such a sulfate capsule has not been achieved yet, although a number of complexes with mono-pyridylurea ligands have been reported in recent years. Moreover, in the complexes of ZnSO4 with the same ligand employed herein (L), the metal ion is coordinated by two or three L molecules, while the sulfate ion participates both in direct coordination with metal ions and hydrogen bonding with urea groups.
The work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The detailed report has been published in Chem. Commun. (Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 2880–2882).
Chem. Commun.Paper
