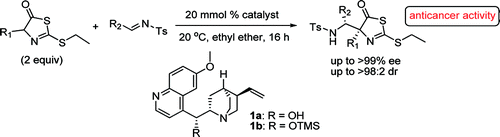
Researchers of Lanzhou University and Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics of the CAS have uncovered that, in the aza-Mannich addition of 2-(ethylthio)-thiazolones andN-tosyl aldimines, the cinchona alkaloid catalyst system could perform efficiently. By establishing a carbon- and nitrogen- substituted quaternary carbon stereocenter, a series of masked chiral 2-(ethylthio)-thiazolone derivatives have been synthesized with high levels of diastereo- (up to>98:2) and enantioselectivities (up to >99%) for the first time. Several new derivatives have been found to show potential anticancer activities. This preliminary study provided a foundation for the further development of new single enantiomer anticancer drugs.
With proven utility in biological chemistry, heterocyclic compounds have received special attention gradually. There are numerous biologically active molecules with five-membered rings, containing two heteroatoms. And the thiazole ring is the most widely existing one. According to the literature, the thiazole ring is an important scaffold associated with several biological active compounds. However, to the best of the researchers’ knowledge, the research on modified thiazolone derivatives has mainly focused on racemic ones. Only one example using 2-benzyloxythiazol-5(4H)-ones as substrates in asymmetric addition was reported by Ooi’s group in 2010. Therefore, the development of new highly efficient organic synthetic methods to access optically active thiazolone derivatives would be of great value for the drug-lead synthesis.
The work ahs been financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the National S&T Major Project of China.
The detailed report has been published in Org. Lett. (Org. Lett., Vol. 13, No. 6, 2011).
Org. Lett.Paper
