Researchers at the CAS Key Laboratory of Chemistry of Northwest Plant Resources of the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics have fabricated a novel silver-coated solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fiber based on electroless plating technique.
The silver coating had very porous structure with large surface area, which enhanced the adsorption ability and increased the extraction efficiency. This fiber was firm and stable, and can be prepared simply and conveniently. The inherent chemical stability of silver and the strong metallic bond between silver coating and stainless steel wire made the fiber exhibit excellent stability and durability to acid, alkali and high temperature. The proposed SPME-GC method showed wide linear ranges for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and phthalate esters (PAEs).
Compared with commercially available fibers and other novel SPME fibers reported lately, the silver-coated fiber kept higher extraction efficiency and lower limit of detection (LODs) towards the same compounds extracted. Single fiber repeatability and fiber-to-fiber reproducibility were both satisfactory. Two real samples was chosen to evaluate the reliability of the silver-coated fiber, several kinds of analytes were detected and quantified.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The findings have been published in Analytica Chimica Acta (Analytica Chimica Acta 701 (2011) 174– 180).
Analytica Chimica ActaPaper
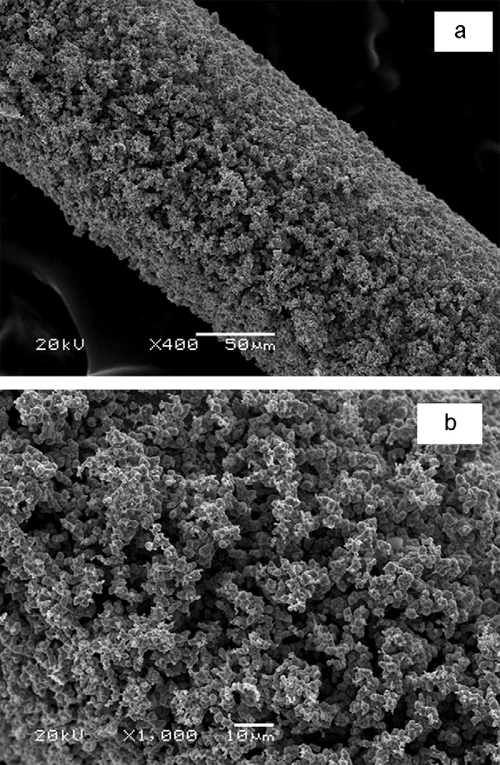
SEM images of the silver-coated SPME fiber at the magnification of (a) 400; (b) 1000.
