A-C:Si:Al carbon-based coatings possess low residual stress, moderately high hardness, good toughness, and controlled tribological moisture sensitivity coupled with low friction coefficient and high wear resistance under different relative humidity conditions, found by researchers at the State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication of the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics.
The result was obtained through a comparative study on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and tribological moisture sensitivity of a-C:Si and a-C:Si:Al coatings.
The good balance between the hardness and toughness, low internal stress, and superior low tribological moisture sensitivity of a-C:Si:Al coating make it a good candidate for solid lubricating coating in engineering applications.
The carbon-based coatings characterized by high hardness, low internal stress, good toughness, and low tribological moisture sensitivity are of continuously increased significance in the engineering applications. Unfortunately, successful applications of carbon-based coatings have been considerably restricted by the high internal stress and poor adhesion to some substrates, especially, they could increase friction coefficient and quickly fail in high humid or aqueous environments. Therefore, many researchers have devoted to the preparation of carbon-based coatings by doping additional elements to overcome those drawbacks.
According to previous studies, the Si and Ai would be also good candidate as a doping additional element in the carbon-based coatings. However, the combination of Si and Al-dopings in carbon-based coatings was scarcely reported.
The work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and National Program on Key Basic Research Project of China (973 Program).
The findings have been published in Tribol Lett (Tribol Lett (2011) 43:329–339).
Tribol LettPaper
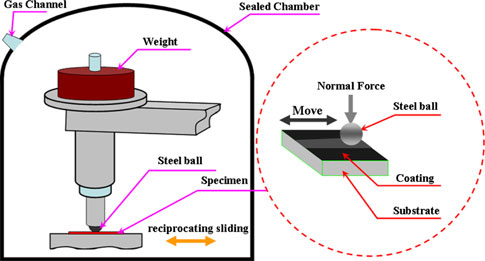
Schematic diagram of wear test for as-fabricated carbon-based coatings
