CdS is one of the most frequently studied metal sulfide photocatalysts due to its narrow band gap (2.4 eV) which allows the absorption of visible light. ZnS is another important semiconductor material investigated for photocatalytic water splitting. Recently, it has been reported that incorporation of ZnS into CdS to form CdxZn1-xS solid solution was one effective way to improve the activity of CdS, because it can make the conduction band edge more negative, resulting in a stronger drive force for water reduction
In order to enhance the activity of CdxZn1-xS solid solution, various metal ions have been doped into the solid solution to improve optical absorption. Researchers at Nanchang University and Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), have prepared Bi3+ doped Cd0.5Zn0.5S photocatalysts by a simple hydrothermal method.
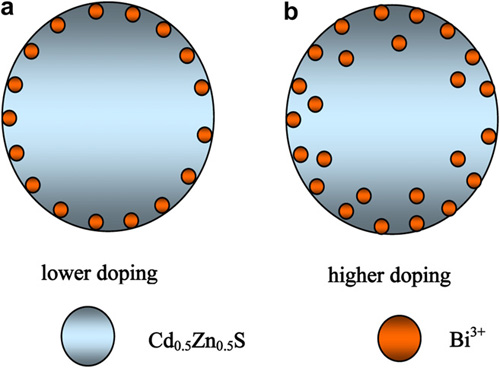 |
| The schematic illustration of the doping depth at/in Cd0.5Zn0.5S with various Bi3Ddoping contents. |
The doping depth can be adjusted by the doping content. When Bi3+ doping content is lower, the doping ions lie at the surface lattice sites, whereas when the doping content is higher, the ions also enter the bulk lattice sites. Bi3+ doping enhances markedly photocatalytic activity. When Bi3+ doping content is 0.10 mole %, the photocatalyst exhibits the highest activity, and the average apparent quantum yield amounts to 9.71% during 30 h under visible-light irradiation (λ≥420 nm).
The work has received support from the National Nature Science Foundation of China, National Basic Research Program of China, Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangxi Province and Research Fund of Education Ministry of Jiangxi, China.
The findings have been published in International Journal of Hydrogen Energy(International Journal of Hydrogen Energy37 (2012) 1366-1374).
