The introduction of martensite with nano-scale twins can improve hardness and wear resistance of Fe70Ni30 alloy, according to a study by researchers at State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
They have first fabricated an Fe70Ni30 alloy with nano-twinned martensitic structures by rapid cooling the product into liquid nitrogen and then investigated the mechanical and tribological properties to evaluate the benefits of twinned structure on the strength and wear resistance improvement of Fe70Ni30 alloy.
 |
|
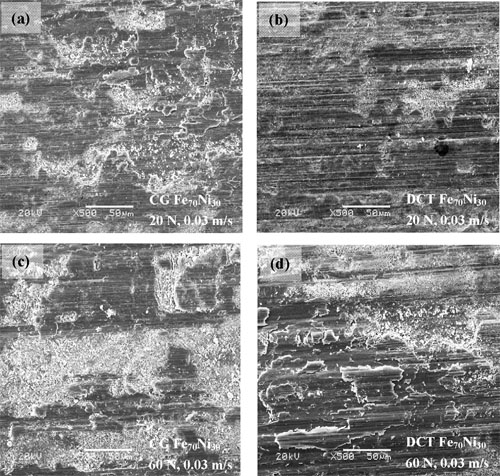
SEM images showing the worn surfaces of CG Fe70Ni30 (a) and DCT Fe70Ni30 (b) under 20 N, CG Fe70Ni30 (c) and DCT Fe70Ni30 (d) under 60 N after sliding for 20 min at sliding speed of 0.03 m/s. |
The results showed that after the introduction of martensite with nano-scale twins, the Vickers hardness of Fe70Ni30 increased from 145 to 248 Hv. The friction coefficient of both samples was almost the same, and it decreased with increasing applied load and increased with increasing sliding speed. The XPS results indicated that oxide protecting film was formed on the worn surface, which may dominate the friction coefficient. The wear rate for both samples increased with increasing applied load and decreased slightly with increasing sliding speed. The wear resistance of DCT-Fe70Ni30 alloy was obviously enhanced. The wear mechanisms for the coarse-grained and nano-twinned Fe70Ni30 alloys change from ploughing and delamination under lower applied load to severe delamination when the load increases.
The work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and National Program on Key Basic Research Project of China (973 Program). The findings have been published in Wear(Wear274– 275 (2012) 395– 400).
