The failure of mechanical components in service can often be attributed to wear, corrosion, and fracture. Wear and corrosion of mechanical components, which has always been the two most pressing problems especially in mechanical engineering fields, not only resulted in enormous loss of energy sources and materials but also pollute the environment. Though some alloys, such as stainless steel, show good corrosion resistance, they lack enough wear resistance due to their low hardness. Therefore, fabricating novel wear and corrosion resistant coating is one of the most economic, effective, and flexible methods to enhance the wear and corrosion performances for many mechanical components working under corrosive conditions.
Researchers at State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), have Ni3Si–Cr7C3 composite coatings showing excellent tribological performances.
They first deposited Ni3Si–Cr7C3 composite coatings with various contents of Cr7C3 on the AISI1020 steel substrate by self-propagating high temperature synthesis casting and studied their tribological performances under water and acid environments. It has been found that the Cr7C3 content has a remarkable influence on the micro hardness of the coatings and the optimal content is 32.2wt.%. The COFs of the coatings under both environments are much lower than that of substrate and AISI321 stainless steel. The COFs are lower under acid environment compared to under water environment because the hydrated silica protection film is much easier to form when the Hþ exists. All of the Ni3Si–Cr7C3 composite coatings exhibit better wear resistance than the substrate and the AISI321 steel both in water and sulfuric acid solution due to the hard phaseCr7C3 suppress and even stop the hydrogen-induced embrittlement. It is noteworthy that the coating containing 37.2wt.% of Cr7C3 expresses the best wear resistance because of its compact and irregular microstructures.
The coatings possess excellent corrosion resistance and have tremendous application prospect in surface protection field.
The work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and National Program on Key Basic Research Project of China (973 Program).
The findings have been published in Tribology International(Tribology International48 (2012)216–225).
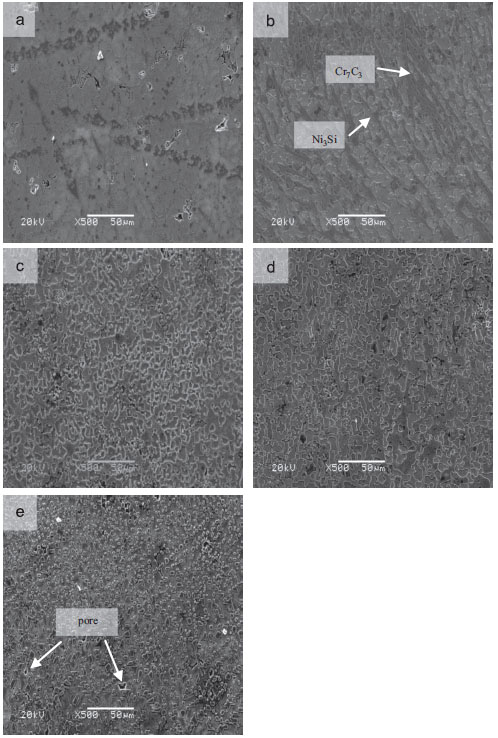
SEM micrographs of the composite coatings with different contents of Cr7C3: (a) NC1, (b) NC2 ,(c) NC3 (d) NC4, and (e) NC5.
