Abstract:
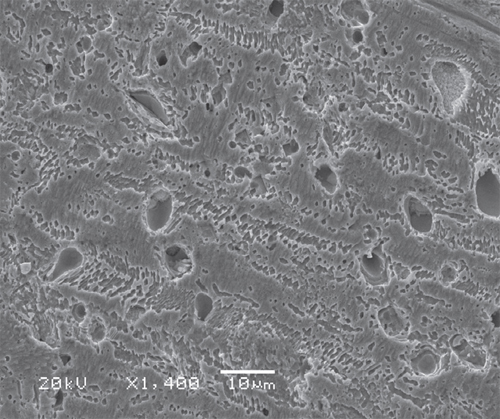
Tribological behaviors of Cu–6Sn–6Zn–3Pb alloy sliding against AISI321 stainless steel under sea water, distilled water and dry sliding conditions are studied on a pin-on-disc tester. Generally, the friction coefficient in distilled water is the largest and the smallest in dry-sliding. However, the wear rate is in the opposite case. The wear mechanism is micro plough and plastic deformation in distilled water and under dry-sliding, but much severe in the latter case. In sea water environment, the wear mechanism is microplough, plastic deformation and corrosion. Sea water and distilled water show a cooling effect in comparison with dry sliding, additionally, sea water also has lubricating and corrosive effects.
Conclusions
1. The testing environment influences the tribological behaviors of bronze 663 considerably. The friction coefficient is the largest in distilled water and the smallest in dry-sliding.
2. The wear mechanism of bronze663 is microplough and plastic deformation in distilled water and under dry-sliding, but much severe in the latter case. In sea water environment, the wear mechanism is microplough, plastic deformation as well as
corrosive.
3. The sea water shows lubricating effect, cooling effect and corrosive effect. Although sea water can reduce the friction coefficient of specimen, it increases the specific wear rate of bronze 663.
Published in Tribology International55 (2012)126–134