Abstract:
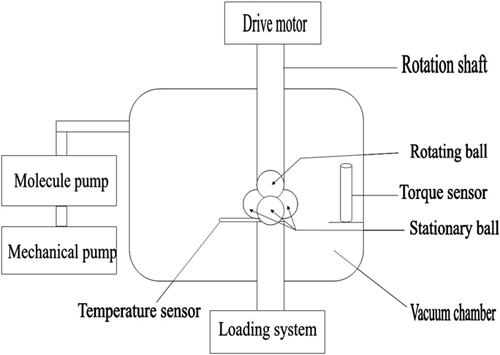
The effect of surface-modified Ag nanoparticles as additives of multialkylated cyclopentanes(MACs) was investigated in air and vacuum by a vacuum four-ball tribometer. The results showed that both the MACs and MACs containing Ag nano particles exhibited steady and low friction coefficients and slight wear in air. However, under vacuum conditions, MACs showed the initial seizure-like high friction, while introducing Ag nano particles could effectively eliminate it. Confirmed by the surface analysis, the improved tribological performances caused by Ag nano particles could be ascribed to the metal Ag boundary film formed on the friction pair surfaces during tests.
Conclusions:
Sliding friction experiments were carried out under vacuum and in air lubricated by MACs and MACs containing Ag nanoparticles. Based on the above experimental results, the following conclusions are drawn:
1. Both the friction coefficients and the WSD values increased remarkably from air to low vacuum then to high vacuum lubricated by MACs base oil.
2. Ag nanoparticles were effective in improving the tribological properties of MACs base oil, especially in eliminating the initial seizure-like high friction under vacuum condition.
3. The tribological mechanism of Ag nanoparticles was the adsorption and deposition of Ag nanoparticles on the friction pair surfaces to form the boundary film, which decreased the shearing stress and effectively inhibited initial high friction under vacuum condition.
4. Ag nanoparticles could be considered as a potential candidate of lubricating oil additives for space application.
Published in Tribology International55(2012)1–6