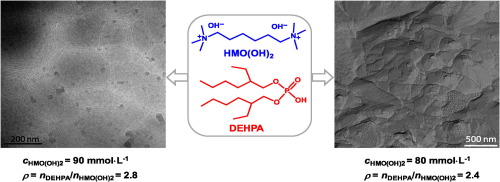
Abstract: Ionic self-assembled structures have been prepared successfully between di-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid (DEHPA) and hexamethonium hydroxide (HMO(OH)(2)). The DEHPA/HMO(OH)(2) complexes show good surface activity at a wide mixing molar ratio of DEHPA to HMO(OH)(2) (rho), within which the critical micellar concentration (cmc) is far below that of any single component. In bulk aqueous solutions, rich phase behavior was observed by varying C-DEHPA and C-HMO(OH)2. When the concentration of HMO(OH)2 is in the range of 10-100 mmol L-1, isotropic L-1 phases, birefringent L-alpha phases and a phase-separated region were successively observed with increasing c(DEHPA). At high c(HMO(OH)2) range (>78 mmol L-1), a narrow L-1/L-alpha two-phase region with the L-alpha phase at the bottom was noticed between the single L-1 and single L-alpha phase regions. The rheological properties of the samples in the single L-alpha phase region at 2.6 <= rho <= 2.8 are quite similar. Cryo-TEM and freeze-fracture TEM (FF-TEM) observations revealed the presence of multilamellar vesicles with flexible and even branched bilayers. At 2.2 <= rho <= 2.6, however, the rheological properties are highly sensitive to rho due to the sophisticated self-assembly behavior as proved by imaging studies and H-2 NMR measurements. Closely-stacked flat structures which look like foams or cellular networks have been newly discovered. Interestingly, NaCl could arouse an L-1 to La phase transition due to the suppression of the effective area of the hydrophilic headgroups of the ionic complexes, leading to an increase of the critical packing parameter p. The viscoelasticity properties of the salt-containing L-alpha, phases decreased with increasing salinity. We hope our research can provide new ideas for the construction of supramolecular materials by surfactant ionic self-assembly (SISA) strategy. Keywords: Surfactant; Ionic self-assembly; L-alpha phases; Rheological properties; Cryo-TEM; FF-TEM Published in JOURNAL OF COLLOID AND INTERFACE SCIENCE, 472 157-166; 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.03.047 JUN 15 2016
|