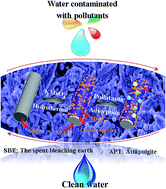
Abstract:Manganese dioxide/carbon/attapulgite ternary composites were fabricated via a facile hydrothermal method based on spent bleaching earth. It is worth noting that the residual organic matter of the spent bleaching earth not only served as a low-cost available carbon precursor, but also as a reductant for the formation of manganese dioxide based on the redox with KMnO4. Using the organic dye of Brilliant green and the heavy metal ion of Pb(II) as model pollutants, the effect of the critical factors on the adsorption properties have been systematically investigated, including the sample preparation conditions, contact time and initial concentration of pollutants. The results reveal that the adsorption properties of the as-prepared composites are well dependent on the concentration of KMnO4, and the maximum adsorption capacity toward Brilliant green and Pb(II) can reach 199.99 mg g(-1) and 166.64 mg g(-1) while the concentration of KMnO4 is 12% and 16%, respectively. KeyWords Plus: HYDROTHERMAL CARBONIZATION PROCESS; HIGH-PERFORMANCE SUPERCAPACITORS; PH-DEPENDENT DEGRADATION; FIXED-BED ADSORPTION; HEAVY-METAL IONS; AQUEOUS-SOLUTION; METHYLENE-BLUE; EFFICIENT REMOVAL; CARBON NANOTUBES; ACTIVATED CARBON Published in RSC ADVANCES, 6 (43):36534-36543; 10.1039/c5ra26362j 2016
|