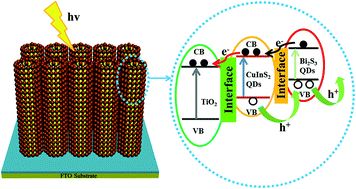
Abstract:The PLD technique is used for the direct fabrication of QD sensitized solar cells (QDSSCs) without any encapsulation and/or resorting to any surface treatment, ligand engineering and/or post-synthesis processing which might involve some toxic chemical regents harmful to the performance of solar cells. In this paper, co-sensitizers of Bi2S3 and CuInS2 quantum dots (QDs) are deposited on TiO2 nanorods via a physical deposition-based pulsed laser deposition (PLD) technique to fabricate the cascade structure of Bi2S3/CuInS2/TiO2. The performance of the QDSSCs with a cascade structure is optimized by adjusting the laser energy, and an energy conversion efficiency of 4.81% is achieved under one sun illumination (AM 1.5, 100 mW cm−2). Besides, the photovoltaic device exhibits high stability in air without any specific encapsulation. The improved performance is attributed to enhanced absorption in the longer wavelength region, quicker interfacial charge transfer and less chance of electron recombination with holes. Moreover, the direct atomic contact by the PLD technique and the cascade structure are also favorable factors for the enhanced photoelectrochemical performance of QDSSCs. KeyWords Plus:SENSITIZED SOLAR-CELLS; TIO2 NANOTUBE-ARRAYS; PHOTOVOLTAIC PROPERTIES; IMPEDANCE SPECTROSCOPY; NANOCRYSTALLINE TIO2; QUANTUM DOTS; EFFICIENCY; BI2S3; CDS; NANORODS Published in RSC ADVANCES, 6 (75):70952-70959; 10.1039/c6ra14901d 2016
|