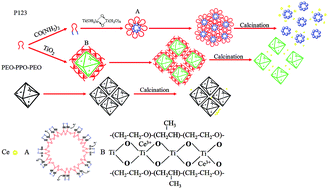
Abstract: Mesoporous ceria-titanium catalysts were synthesized by one pot hydrothermal method and used for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO with nearly complete NO conversion over a wide operating temperature range. The outstanding activity of the ceria-titanium catalyst was attributed to the tunable particle size and the efficient control of surface areas and pore volume in the range of 260-400 degrees C by the modulation of the soft template content. Especially, ceria oxide (CeO2) active centers being highly dispersed and titanium oxide (TiO2) with sufficient surface areas and uniform pore canals are the main reasons for the excellent SCR performance. For a series of catalysts, H-Ce0.2TiOx-2 exhibited nearly complete NO conversion (99%) in the range of 260 degrees C to 400 degrees C, with excellent stability and desired resistance to H2O. In addition, we discussed the reaction and deactivation mechanisms of ceria-titanium catalysts for the SCR, resulting from better redox ability and abundant acid sites. In view of the simple process and outstanding stability of mesoporous ceria-titanium catalysts, this could be treated as an ideal candidate for real applications. KeyWords Plus:LOW-TEMPERATURE; CARBON NANOTUBES; CE/TIO2 CATALYST; NH3; AMMONIA; CEO2; OXIDATION; OXIDE; SPECTROSCOPY; PERFORMANCE Published in RSC ADVANCES, 6 (80):10.1039/c6ra17840e 2016 |