XIONG Ya-hong SU Jian-hong LIU Xiao-ping
(Institute of Biomaterial, College of Science, South China Agricultural University, guangzhou 510642, China)
Abstract: Pocine pancreas lipase (PPL) was modified with phthalic anhydride (PA) and the average amino modification yield was determined by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid. Ultra violet spectrum and fluroscence spectrum of modified lipase PA-PPL were compared with those of unmodified lipase PPL. Effects of pH and temperature on hydrolysis activities and stabilities of PA-PPL and PPL were studied by kinetic method and series of kinetic and thermodynamic parameters were calculated. The experimental results showed that the average amino modification yield was 30% under the experimental conditions. After PPL was modified by PA, red shift of PPL’s characteristic ultraviolet peak and absorbance decrease occurred and blue shift of fluroscence emission peak and fluroscence intensity incrase were taken place. After PA modification, PPL’s optimal pH and temperature for catalysis weren’t changed and these values were pH 7.5 and 40 ℃ respectively. Chemical modification of PPL with PA caused that catalysis efficence and substrate affinity were enhanced and all of activation energy (Ea) and activation free energy (ΔG≠) and activation enthalpy (ΔH≠) and activation entropy (ΔS≠) for catalysis decreased obviously. For example, turnover number (kcat) and activation energy (Ea) under the optimal conditions for hydrolysis of PA-PPL and PPL were 39.8s-1, 25.8 kJ/mol and 34.4s-1, 43.8 kJ/mol respectively. Chemical modification of PPL with PA also resulted that the values of thermodynamic parameters for thermal denaturation, such as activation energy (Ea,d), activation free energy (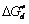 ), activation enthalpy (
), activation enthalpy ( ) and activation entropy (
) and activation entropy ( ) for denaturation, increased markedly and the half-life time (t1/2) became longer. So PA modification also enhanced thermal stability of PPL.
) for denaturation, increased markedly and the half-life time (t1/2) became longer. So PA modification also enhanced thermal stability of PPL.
Key words: Lipase; Chemical modification; Stability; Kinetics; Thermodynamic paraments
E-mail: xiongyahong@scau.edu.cn
Journal of Molecular Catalysis, Vol. 24, Issue 5, 2010, 435~442
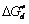 ), activation enthalpy (
), activation enthalpy ( ) and activation entropy (
) and activation entropy ( ) for denaturation, increased markedly and the half-life time (t1/2) became longer. So PA modification also enhanced thermal stability of PPL.
) for denaturation, increased markedly and the half-life time (t1/2) became longer. So PA modification also enhanced thermal stability of PPL.