Researchers of the State Key Laboratory for Oxo Synthesis and Selective Oxidation, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, CAS, have made progress in the research on palladium-catalyzed C-H bond activation. The research result has been published in Journal of the American Chemical Society (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 3650-3651. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ja910104n) as a communication and attracted wide attention.
With the support of the CAS and National Natural Science Foundation, the research group head by Prof. XIA Chungu and Prof. HUANG Hanmin reported an efficient protocol for the generation of amines by palladium catalyzed nucleophilic benzylic addition of 2-methyl substituted azaarenes to N-sulfonyl aldimines under netural conditions via C-H bond activation by taking advantage of the orientated positioning of heteroatom. The protocol is efficient and atom-economical and target products with high yield can be obtained via only one step. The N-heterocyclic amine and heterocyclic compounds with isoindoline-based pigment structure are prodrugs with physiological activity. The protocol has the potential to be applied in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and natural products.
C-H bond is one of the most common functional groups among organic compounds. The chemical synthesis based on C-H bond activation needs only simple starting materials and the reaction process can be shortened as well. Moreover, with the synthesis method, target products which can not be achieved via normal ways can be obtained. Thus it is the most economical, facile and efficient way and is in line with the developing trend of the green synthetic chemistry. The synthesis of C-C and C-X bonds through C-H bond activation has attracted much attention from organic chemists.
However, C-H bond activation has still been a big challenge due to its high bond energy, low polarity, difficulty in activation, low reactivity and difficulty in efficient transformation. In recent years, much effort has been devoted to high atom-economical synthesis of target products via C-H bond activation using simple reactants under mild conditions.
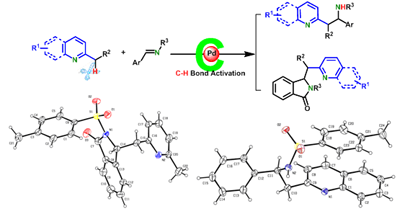
Palladium-catalyzed C-H bond activation


