Researchers at the R&D Center of Lubricating and Protecting Materials of the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, CAS (LICP, CAS) have prepared two nickel-based high temperature wear resistant coatings, namely NiCrBSi coating and NiCrBSi/WC-Ni composite coating, on stainless steel by laser cladding.
Results show that these two types of laser cladding coatings have higher microhardness and high temperature wear resistance than the stainless steel substrate. Especially, laser cladding NiCrBSi/WC-Ni composite coating shows better high temperature wear resistance than NiCrBSi coating, which is attributed to the formation of hard WC phase after laser cladding. The wear mechanisms of stainless steel under high temperature are adhesive wear, abrasive wear and severe plastic deformation. The wear mechanism of the laser cladding coatings under high temperature is mild adhesive wear and abrasive wear.
Laser cladding is an advanced surface engineering technology. With laser beam as the heat source, it can make cladding materials melt simultaneously on both substrate surface and substrate surface thin film. The cooling rate is high and metallurgical bonding between coating and substrate when solidifying can be realized. With laser cladding, amorphous and nano-crystalline structures and other special structures can be formed and selective cladding can be realized. It is of low dilution rate and easy to be automatically controlled.
The work has received support from the National High-tech R&D Program of China, Main Direction Program of Knowledge Innovation of Chinese Academy of Sciences and National Natural Science Foundation of China. The detailed report has been published in Wear (Wear 270 (2011) 492–498).
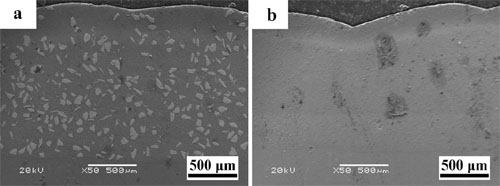
Cross-sectional SEM morphologies of (a) NiCrBSi/WC-Ni composite coating and (b) NiCrBSi coating.(Image by ZHOU Jiansong et al.)
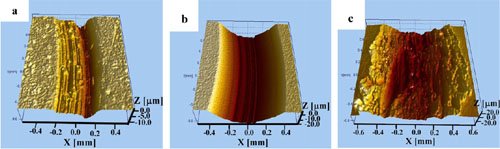
3D non-contact surface mapping of the wear scars of (a) NiCrBSi/WC-Ni composite coating, (b) NiCrBSi coating, and (c) stainless steel sliding.(Image by ZHOU Jiansong et al.)


