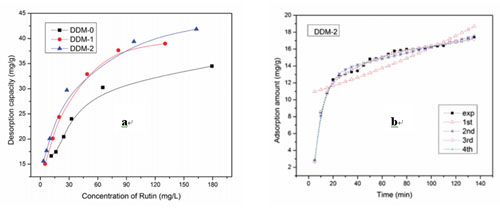
Adsorption behavior of the modified MARs (a) Desorption capacities of rutin on modified MARs (b) Regression curves of the relationship between adsorption amount and time (Image by DI Duolong et al.)
Macroporous adsorption resins (MARs) have been shown to be potentially powerful separation materials and have been applied in many fields. To gain a greater adsorption capacity and a higher adsorption selectivity for some specific organic compounds, chemical modification of MARs is often undertaken by introducing special functional groups into the matrix of the polymeric adsorbents. Thus, investigation on the adsorption features of organic compounds on MARs is of great importance. However, researchers all over the world have always paid attention to the application of MARs, and theoretical research on the adsorption features of MARs lags far behind.
Researchers at the CAS Key Laboratory of Chemistry of Northwestern Plant Resources, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP) have synthesized a series of MARs with novel structure and functional groups on the basis of the Friedel-Crafts catalyzed and amination reaction. They has systematically investigated the adsorption feature of the synthetic resins with respect to the purification effect by employing rutin as the adsorbate.
Different from traditional adsorption patterns, the results showed interesting conclusions: (1) With the increase in the temperature of the experiment, the adsorption capacity increased gradually; with the increase in the concentration of the initial solution, the adsorption capacity increased to the maximum and then decreased gradually. (2) The classical models that the inductive effect transmitted to the first layer and the adsorption process contained in one compartment could not explain our experimental results reasonably. Thus, researchers have proposed a new adsorption isotherm model that the inductive effect passed on to a higher layer and a new adsorption kinetics model in which the adsorption process contained more compartments were created according to the multiparameter theory and Karickhoff’s theory by investigating the regression of the experimental results. They have concluded that the inductive effect passed to the fourth layer and the adsorption process contained four compartments.
It is expected the study will benefit the development of an efficient, successful purification process and the synthesis of MARs with high selectivity.
The work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, no. 20974116). The findings have been published in Langmuir (Langmuir, 2011, 27(15), 9314-9326).


