Macroporous absorption resin (MAR) is one of the key technologies in the modernization and industrialization of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM).At present, the research on MAR mainly focuses on its adsorption kinetics and adsorption thermodynamics. Little attention has been given to the structure-activity relationship between MAR and target molecule and the separation principle of MAR.Therefore, there lack theoretical guidance for the design and synthesis of MAR, which in turn leads to poor selectivity and specificity of MAR. Moreover, it takes much effort to select MAR which has the best separation efficiency for target molecule.These factors have become problems to be urgently solved in the interdisciplinary subject between functional polymer and natural pharmaceutical chemistry.
Researchers at the Key Laboratory of Chemistry of Northwestern Plant Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), have been engaged in the research on the separation principle and application of MAR for years. Applying methods in computational chemistry, they have established several mathematical models for MAR adsorption, including multilayer adsorption force model, multilayer adsorption kinetic model, multi-layer and multi-parameter adsorption kinetic model, etc. Furthermore, they have applied these models in guiding and predicting the separation and extraction methods of active components from natural products, such as extraction of flavonoids from leaves of Hippophae rhamnoides Linn.
Their work has received support from the CAS. The findings have been published in the following journals.
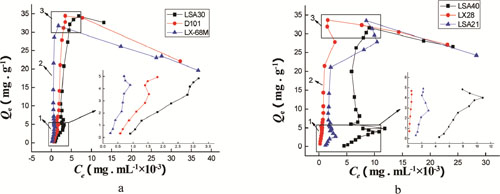
Capillary effect during the absorption process of MAR (Image by DI Duolong et al.)
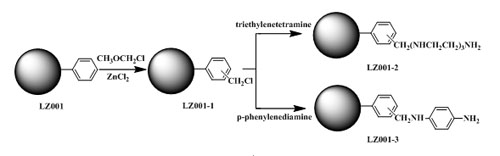
Reaction scheme for the preparation of functionalized MAR(Image by DI Duolong et al.)
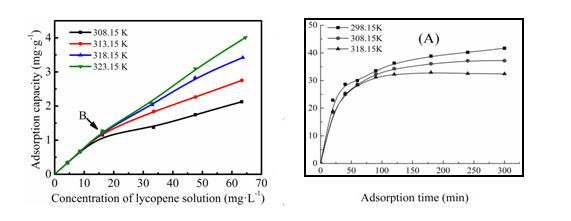
Adsorption isotherm of Lycopene Adsorption kinetic curve of (?)-epigallocatechin
on MAR (Image by DI Duolong et al.) gallate (EGCG) on MAR (Image by DI Duolong et al.)
J Appl Polym Sci(2012, 2: 903–912)
Sep Purif Technolo(2012, 89: 22–30)
Food Chem( 2012, 132: 268-276)
J Agric Food Chem(2012, 60: 1555-1566)
Fundam Chem Engin(2011, 233-235: 2893-2897)
J Sci Food Agric(2011, 91: 2826-2834)
J Agric Food Chem(2011, 59: 9629-9636)
J Polym Mater( 2010, 1: 75-92)


