Direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs) have drawn great attention due to their simple structure, quick start-up under low temperature, high energy-conversion efficiency and energy density, low operating temperature, low-to-zero pollutant emission, as well as the simple handling and processing of the fuel. They can be applied in uninterrupted communication devices and portable electronic products. However, the high cost of anode catalysts has limited the application of DMFCs. The solution to this problem is to use appropriate supports and design the structure of the catalysts .
The low dimensional materials and chemical energy storage research group at the Laboratory of Clean Energy Chemistry and Materials, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has developed a facile and environmental-friendly way to synthesize graphene supported dendritic PtNi bimetallic catalysts using Ni nanopaticles as the seeds and reducing agent. The as-made d-PtNi/G catalyst shows very large electrochemical active area (ECSA) and excellent electrochemical activity and stability toward methanol oxidation. Especially, its electrochemical activity is much higher than those of the commercial Pt/C and PtRu/C catalysts for methanol electrooxidation. Compared with noble bimetallic (Pt-Au, Pt-Pd, Pd-Ru) nanodendritic catalysts, the PtNi nanodendrites are low in cost and simple in preparation. The work has been published in Electrochem. Commun.(2012, 23, 72–75).
In addition, the group has synthesized graphene supported hollow PtSnCo nanospheres electro-catalysts and prepared functionalized graphene nanosheets (GNSs) by poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDA) and used them as support material for in situ deposition of Pt nanoparticles. Both of them show excellent catalytic activity. The work has been published in J. Power Sources(2012, 205, 239– 243) and Electrochim. Acta(2012, 59, 429– 434).
The above work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
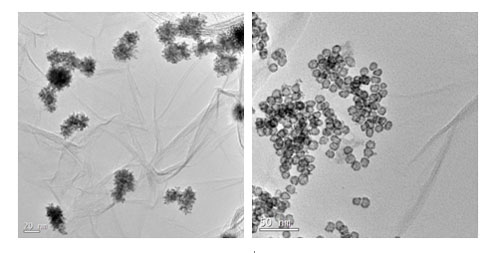
TEM images of the graphene supported dendritic PtNi (d-PtNi/G, left) and hollow PtSnCo catalyst (right) (Image by YAN Xingbin et al.)
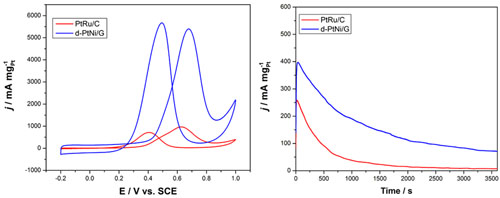
The activity (left) and stability (right) of the commercial PtRu/C and the d-PtNi/G catalysts for methanol electrooxidation (Image by YAN Xingbin et al.)


