Diethylstilbestrol(DES), a non-steroidal hormone, has been used to treat gynecological diseases and promote animal growth. However, DES and its metabolites remain in animal tissues, organs, and excreta; enter the external environment; become environmental estrogen; and then are passed to consumers through the food chain, which can cause cancer in humans. Thirty years of extensive research show that DES residues in the human body and environment have obvious detrimental effects; thus, many countries have banned the use of DES. Nevertheless, various other substitutes that can promote animal growth do not have as much potency as DES, so the use of DES in animal production is prohibited but has not completely stopped. Mainly due to economical interests, the abuse in the use of DES continues. Therefore, an efficient and sensitive method for the determination of DES should be established to monitor DES residues in food and thereby to ensure the safety of food supply.
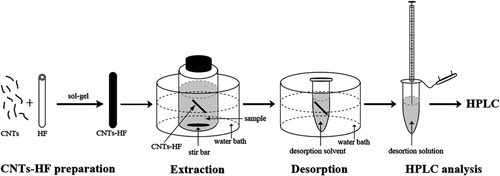
Researchers from the Key Laboratory of Chemistry of Northwestern Plant Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, have developed a novel method of carbon nanotube-reinforced hollow fiber solid-phase microextraction (CNTs-HF-SPME) coupled with high performance liquid chromatography and applied it to determine DES in milk samples for food quality control.
 |
|
Schematic illustration of CNTs-HF-SPME combined with HPLC. (Image by SHI Yanping et al.) |
In their work, the wall pores of hollow fibers were filled with MWCNTs using sol–gel technology. Hollow fibers can prevent large molecules, such as proteins, from entering small pores. The MWCNTs in the wall pores of the hollow fiber can absorb target molecules, thus effectively and selectively extracting DES from milk products. After the optimization of the extraction conditions for DES, effective sample clean-up, good linearity, and recovery were obtained. Results of the present experiments showed that CNTs-HF-SPME combined with HPLC is a simple, rapid, and cost-effective technique to monitor DES residues in milk products.
The work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The findings have been published in Talanta(Talanta97(2012)222–228).


