Stimuli-responsive hydrogels not only express excellent biocompatibility, but also can respond when exposed to external stimulation, enabling a wider range of applications in biomedicine. However, at present, stimuli-responsive hydrogel still has some disadvantages such as poor mechanical properties and limited response to a single stimulus. There is a great need for stimuli-responsive hydrogels with excellent mechanical properties and capability to respond to multiple stimuli.
Recently, the team led by WANG Qihua and WANG Tingmei from the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, issued a report on 4D printing of dual-stimuli response alginate hydrogel. These hydrogel structures were directly printed with high structural accuracy, following which the hydrogels were immersed in Ca2+ solution and chitosan solution respectively. The 4D printed hydrogels were able to perform step-wise volume contraction.
The soaking strategy adopted was able to not only achieve step-wise volume contraction of the sodium alginate structure, but also continuous enhancement of the mechanical properties of alginate hydrogel with continuous immersion in two solutions. The printed structures were able to be used for loading-unloading experiments 5 times and support an object which weighs 361 times its own weight.
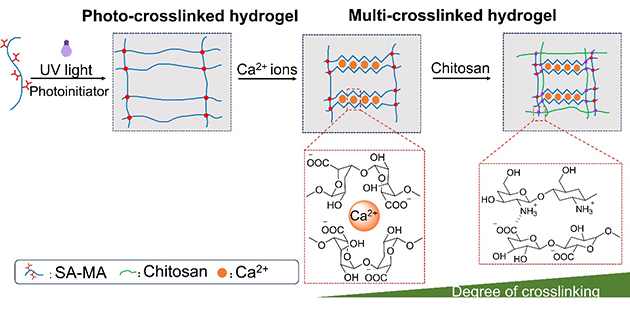
Figure 1. The deformation mechanism of alginate hydrogel.
Relevant research was published in ACS Applied Polymer Materials (DOI: 10.1021 / acsapm. 1c01034).
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Qingdao University.
Contact:
ZHANG Yaoming
Email: yaomingzhang@licp.cas.cn
Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics


