Abstract
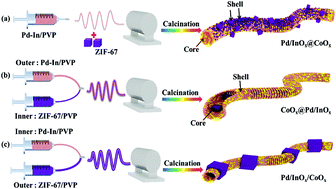
In this work, Pd/InOx@CoO(x)core-shell nanofibers, CoOx@Pd/InO(x)core-shell nanofibers and Pd/InOx/CoO(x)nanofibers with different morphologies have been successfully synthesized for the catalytic combustion of toluene. Among them, the Pd/InOx@CoO(x)core-shell sample is novel and composed of Pd/InO(x)nanotube cores, CoO(x)nanocubes and CoO(x)nanoparticle shells derived from ZIF-67. On the contrary, the CoOx@Pd/InO(x)core-shell catalyst is assembled by CoO(x)nanocube cores and Pd/InO(x)nanotube shells. Finally, the Pd/InOx/CoO(x)nanofibers as references are synthesized by a method similar to the synthesis of the CoOx@Pd/InO(x)core-shell sample. Interestingly, the Pd/InOx@CoO(x)core-shell sample displayed the best activity for toluene oxidation withT(90)= 253 degrees C, good thermal stability and good cyclic stability during three runs. Through some characterizations, it was verified that the Pd/InOx@CoO(x)core-shell sample exhibited the best performance for toluene oxidation reactions due to a larger specific surface area, higher reducibility, more abundant structural defects and oxygen vacancies, higher proportion of Pd(0)and Co(3+)species and higher lattice oxygen species than others. Simultaneously, the Pd/InOx@CoO(x)core-shell sample exhibited good thermal stability and cyclic stability, which might be due to the layer of the CoO(x)shell to protect the stability of the Pd nanoparticle core.
KeyWords Plus:TEMPERATURE CO OXIDATION; IN-SITU; OXYGEN REDUCTION; ADSORPTION STRENGTH; SHELL NANOFIBERS; FACILE SYNTHESIS; CARBON-FIBERS; CO3O4; IN2O3; OXIDE
Published in NANOSCALE,Volume 12;10.1039/d0nr02334e,JUN 14 2020


