Abstract
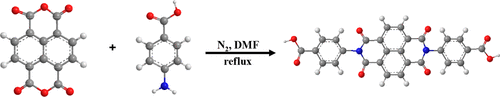
In this paper, Co3O4 was synthesized using pyrolysis of Co-L3, which was prepared by a solvothermal method at different temperatures using a naphthalimide derivative (L3) and cobaltous acetate. The L3 ligands were synthesized using a precursor of naphthalene-1,4,5,8-tetracarboxylic acid and p-aminobenzoic acid. Co-L3-120, Co-L3-160, and Co-L3-200 displayed respectively a one-dimensional (1D) rod structure, a two-dimensional sheet structure, and a 1D spindle structure due to the different structure units. After pyrolysis, the Co3O4 catalysts maintained the same morphologies of the corresponding Co-L3, which was made up of granulum. The Co3O4-160 catalyst presented superior catalytic performance for catalytic combustion of toluene due to the higher redox properties, abundant surface active sites and active oxygen species, higher oxygen vacancies, and higher surface acidities. Further, Co3O4-160 had excellent repetitiveness in three cycling tests and outstanding stability of thermal and moisture resistance.
In this paper, Co3O4 was synthesized using pyrolysis of Co-L3, which was prepared by a solvothermal method at different temperatures using a naphthalimide derivative (L3) and cobaltous acetate. The L3 ligands were synthesized using a precursor of naphthalene-1,4,5,8-tetracarboxylic acid and p-aminobenzoic acid. Co-L3-120, Co-L3-160, and Co-L3-200 displayed respectively a one-dimensional (1D) rod structure, a two-dimensional sheet structure, and a 1D spindle structure due to the different structure units. After pyrolysis, the Co3O4 catalysts maintained the same morphologies of the corresponding Co-L3, which was made up of granulum. The Co3O4-160 catalyst presented superior catalytic performance for catalytic combustion of toluene due to the higher redox properties, abundant surface active sites and active oxygen species, higher oxygen vacancies, and higher surface acidities. Further, Co3O4-160 had excellent repetitiveness in three cycling tests and outstanding stability of thermal and moisture resistance.
KeyWords Plus:AEROBIC OXIDATION; CO3O4; NANOPARTICLES; COMBUSTION; PYROLYSIS; MOFS
Published in CRYSTAL GROWTH & DESIGN;Volume: 20;10.1021/acs.cgd.0c00003,SEP 2 2020


