Abstract
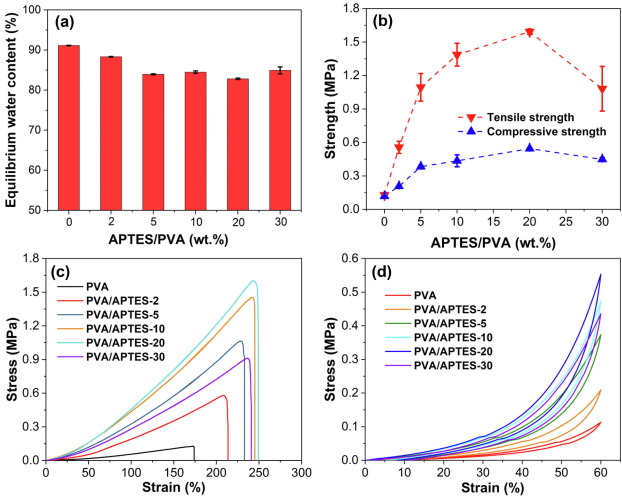
This study aims to reveal a novel approach to synthesize high strength polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) physical hydrogel through the freezing-thawing method, with gamma-aminopropyl triethoxysilane agent as an auxiliary factor. It was shown that the synthesized PVA-based hydrogels had high water content, excellent mechanical properties, and good biocompatibility. The saline agent gamma-aminopropyl triethoxysilane in PVA solution was hydrolyzed and polymerized into NH2-decorated polysiloxane structures, which could be anchored to the porous PVA network and acted as a very effective hydrogen bond acceptor/donor, and thereby arousing a large increase in strength and toughness of PVA hydrogels. Meanwhile, the hydrophobic polysiloxane structures also increased the crystal cross-linking of PVA network and promoted a well-distributed porous PVA network. This work provides a simple and efficient route to synthesize high strength PVA-based physical hydrogel with desirable structure and properties. (C) 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Published in MATERIALS LETTERS,Volume 290;10.1016/j.matlet.2021.129505,MAY 1 2021


