Abstract
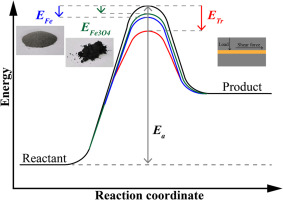
The tribochemical reaction rate of multiply alkylated cyclopentane (MAC) was studied from the perspective of tribo-oxidation. The activation energy of MAC oxidation reaction and respective decrease of activation energy owing to catalysis from iron and Fe3O4 were determined by means of auto-oxidative tests. The sum of the reduced activation energy due to iron and Fe3O4 was less than that in tribological test, which highlighted the crucial role of shear stress in accelerating tribo-oxidation reaction. Additionally, the experimental process was replicated by utilizing reactive molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The simulation results revealed the significance of shear stress in tribo-oxidation reaction and the catalytic mechanism of iron, Fe3O4, and shear stress for promoting oxidation reaction was interpreted.
Keywords Plus:FORCE-FIELDADSORBED MOLECULESDIFFERENT REGIMESMECHANOCHEMISTRYCARBONWEAROILLUBRICATIONDEGRADATIONDYNAMICS
Published in TRIBOLOGY INTERNATIONAL,Volume 165;10.1016/j.triboint.2021.107289,JAN 2022


