Abstract
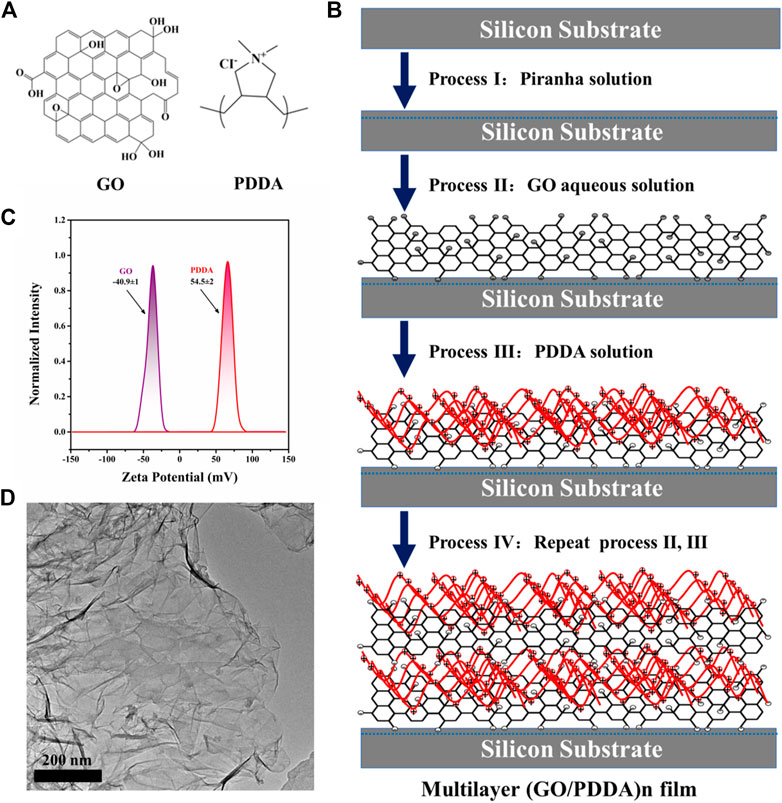
Taking advantage of the strong charge interactions between negatively charged graphene oxide (GO) sheets and positively charged poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDA), self-assembled multilayer films of (GO/PDDA)(n) were created on hydroxylated silicon substrates by alternating electrostatic adsorption of GO and PDDA. The formation and structure of the films were analyzed by means of water contact angle measurement, thickness measurement, atomic force microscopy (AFM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Meanwhile, tribological behaviors in micro- and macro- scale were investigated by AFM and a ball-on-plate tribometer, respectively. The results showed that (GO/PDDA)(n) multilayer films exhibited excellent friction-reducing and anti-wear abilities in both micro- and macro-scale, which was ascribed to the special structure in (GO/PDDA)(n) multilayer films, namely, a well-stacked GO-GO layered structure and an elastic 3D crystal stack in whole. Such a film structure is suitable for design molecular lubricants for MEMS and other microdevices.
Taking advantage of the strong charge interactions between negatively charged graphene oxide (GO) sheets and positively charged poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDA), self-assembled multilayer films of (GO/PDDA)(n) were created on hydroxylated silicon substrates by alternating electrostatic adsorption of GO and PDDA. The formation and structure of the films were analyzed by means of water contact angle measurement, thickness measurement, atomic force microscopy (AFM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Meanwhile, tribological behaviors in micro- and macro- scale were investigated by AFM and a ball-on-plate tribometer, respectively. The results showed that (GO/PDDA)(n) multilayer films exhibited excellent friction-reducing and anti-wear abilities in both micro- and macro-scale, which was ascribed to the special structure in (GO/PDDA)(n) multilayer films, namely, a well-stacked GO-GO layered structure and an elastic 3D crystal stack in whole. Such a film structure is suitable for design molecular lubricants for MEMS and other microdevices.
Keywords Plus:CHEMICAL-REDUCTIONOXIDEGRAPHITELAYERTRIBOLOGYALKYLSILANEMONOLAYERSNANOSHEETSFRICTIONSHEETS
Published in FRONTIERS IN CHEMISTRY,Volume 9;10.3389/fchem.2021.740140,NOV 29 2021


