Abstract
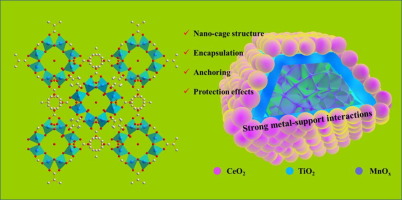
A nanocage-confined composite catalyst TiO2@CeMnOx-NC was carefully designed and fabricated by directional hydrolytic etching of MIL-125. With the directional protection of tannic acid and PVP used as stabilizer agents, MIL-125(Ti) was controllably etched from its inside out by self-hydrolysis. Notably, MnOx was encapsulated into the cavity of the TiO2 nanocage, and CeO2 was mainly anchored on its outside surface. With the help of related characterization methods, it was found that amorphous TiO2 formed after annealing, and fluorite cubic structured CeO2 inhibited the crystallization of MnOx clusters. Thanks to this unique structure, strong metal-support interactions occurred between Ce/Mn oxides and TiO2, which dramatically enhanced its surface acidity and adsorption ability. Besides, the redox capacity has also been significantly affected. Consequently, the carefully designed composite confined TiO2@CeMnOx-NC with a nanocage structure showed excellent NH3-SCR catalytic performance over a wide working temperature window. In addition, benefiting from the double protection of TiO2 nanocages and CeO2 on the outer surface, the MnOx encapsulated in the cavity could be effectively protected from the influence of water vapor in the flue gas, thus exhibiting good water resistance. In situ DRIFTs analysis revealed that the NH3-SCR process on TiO2@CeMnOx-NC mainly followed the Eley-Rideal (E-R) reaction mechanism. Comparing with nanosheets TiO2@CeMnOx-NS and nanoparticles TiO2@CeMnOx-NP, the nanocages TiO2@CeMnOx-NC have more promising prospects in NH3-SCR applications.
Keywords Plus:NOPERFORMANCENH3-SCRCERIUMSO2NH3MECHANISMSCR
Published in CHEMICAL ENGINEERING JOURNAL,Volume432,10.1016/j.cej.2021.134236,MAR 15 2022


