Abstract
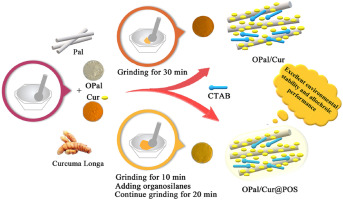
In this study, novel multifunctional durable intelligent hybrid pigments with allochroic, antibacterial, and superhydrophobic properties were facilely fabricated by a cleaner mechanochemical method, in which palygorskite was initially modified with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide to anchor curcumin by semidry grinding, and subsequently coated with organosilanes by one-step modification via semidry grinding. The obtained hybrid pigments were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, transmittance electron microscopy, EDS mapping, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller method. The density functional theory calculation was also performed to further explore the possible interaction among curcumin and organo-palygorskite. The results confirmed that curcumin was loaded on organo-palygorskite via electrostatic and hydrogen bond interactions. Due to the synergistic effect of the organic modification, the obtained hybrid pigments exhibited excellent antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus with minimal inhibitory concentrations of 0.5 mg/mL. Furthermore, curcumin-loaded organo-palygorskite presented excellent thermal and chemical stability after subsequent modification with organosilanes at different heating temperatures and chemical reagents. The organo-palygorskite/curcumin@polymerized organosilane composites could intelligently monitor fish spoilage in real time based on the reversible allochroic properties of the loaded curcumin. Thus, hybrid pigments are expected to design promising multifunctional food packaging materials with allochroic, antibacterial, and superhydrophobic properties.
In this study, novel multifunctional durable intelligent hybrid pigments with allochroic, antibacterial, and superhydrophobic properties were facilely fabricated by a cleaner mechanochemical method, in which palygorskite was initially modified with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide to anchor curcumin by semidry grinding, and subsequently coated with organosilanes by one-step modification via semidry grinding. The obtained hybrid pigments were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, transmittance electron microscopy, EDS mapping, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller method. The density functional theory calculation was also performed to further explore the possible interaction among curcumin and organo-palygorskite. The results confirmed that curcumin was loaded on organo-palygorskite via electrostatic and hydrogen bond interactions. Due to the synergistic effect of the organic modification, the obtained hybrid pigments exhibited excellent antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus with minimal inhibitory concentrations of 0.5 mg/mL. Furthermore, curcumin-loaded organo-palygorskite presented excellent thermal and chemical stability after subsequent modification with organosilanes at different heating temperatures and chemical reagents. The organo-palygorskite/curcumin@polymerized organosilane composites could intelligently monitor fish spoilage in real time based on the reversible allochroic properties of the loaded curcumin. Thus, hybrid pigments are expected to design promising multifunctional food packaging materials with allochroic, antibacterial, and superhydrophobic properties.
Keywords Plus:MAYA-BLUEANTIOXIDANTFUNCTIONALIZATIONMONTMORILLONITESOLUBILITYSTABILITYCOATINGSRAMANCLAY
Published in DYES AND PIGMENTS,Volume203;10.1016/j.dyepig.2022.110359,JUL 2022


