Abstract
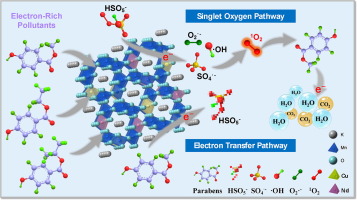
Non-radical oxidation processes with singlet oxygen (O-1(2)) and mediated electron transfer have emerged as efficient methods for the selective degradation of aqueous pollutants in peroxymonosulfate (PMS)-based catalytic systems. On this basis, in this study, transition- and lanthanide-metal co-doped manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieve (Cu-Nd-OMS-2) was synthesized, characterized, and tested in the degradation of aqueous parabens. Methylparaben (30 mg/L) was degraded at 100% and mineralized at 92% within 40 min in the presence of Cu-Nd-OMS-2 and PMS (200 mg/L) in pH scale ranging from 3 to 8. Compared with pristine and mono-doped catalysts, the Cu-Nd-OMS-2, produced by the doping strategy, exhibited a superior catalytic activity for the oxidative degradation of several parabens through turning the mechanism with radicals into non-radical pathway. Electron paramagnetic resonance, quenching experiments and mechanism study indicated that O-1(2) and mediated electron transfer contributed to the removal of parabens. Besides, the redox cycle of Mn(III)/Mn (IV) might be responsible for PMS activation, and abundant surface hydroxyl groups as well as oxygen vacancies on the catalyst further promoted the adsorption of pollutants and the generation of O-1(2). Overall, the present study provides a novel and facile doping strategy on manganese oxide catalysts for fine-tuning radical/non-radical processes towards PMS-based water remediation.
Keywords Plus:BISPHENOL-ASINGLET OXYGENPERSULFATE ACTIVATIONORGANIC CONTAMINANTSHIGH-PERFORMANCEOXIDATIONPEROXYMONOSULFATECHROMATOGRAPHYMECHANISMSFISH
Published in CHEMICAL ENGINEERING JOURNAL,Volume442;10.1016/j.cej.2022.136180,AUG 15 2022


