Abstract
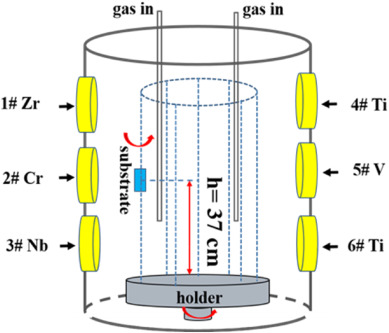
High-entropy ceramic (TiCrZrVNb)C films were deposited by multi-arc ion plating under various acetylene ratios Rc (0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2). The phase composition, microstructure, mechanical properties, and tribological properties of all the films were characterized. The results showed nearly equiatomic compositions for all the metallic elements in all the films, which was consistent with the concept of high entropy. An XRD analysis revealed that the films deposited under Rc of 1 and 1.5 had a simple face-centred cubic (FCC) structure, whereas the films deposited under Rc of 0, 0.5, and 2 exhibited amorphous and second phases, respectively. With increasing the Rc for deposition, the hardness and elastic modulus of the films first increased and then decreased, where the highest values of 27.08 +/- 0.58 GPa and 349.20 +/- 33.78261 GPa, respectively, were obtained for Rc = 1. In addition to exhibiting the highest hardness and elastic modulus, this film also exhibited the best elastic recovery of 55.8%. All the films, except for the alloy film deposited under Rc = 0, exhibited low friction co-efficients and good wear resistance during friction tests. In particular, the film deposited under Rc = 1, exhibited excellent wear resistance with a minimum wear rate of 1.6 x 10(-6) mm(3)/(N.m), which was attributed to a low friction coefficient of 0.11 and outstanding mechanical properties.
Keywords Plus:CARBIDECOATINGSALLOYSMICROSTRUCTURES
Published in CERAMICS INTERNATIONAL,Volume48;10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.03.211,JUL 1 2022


