Abstract
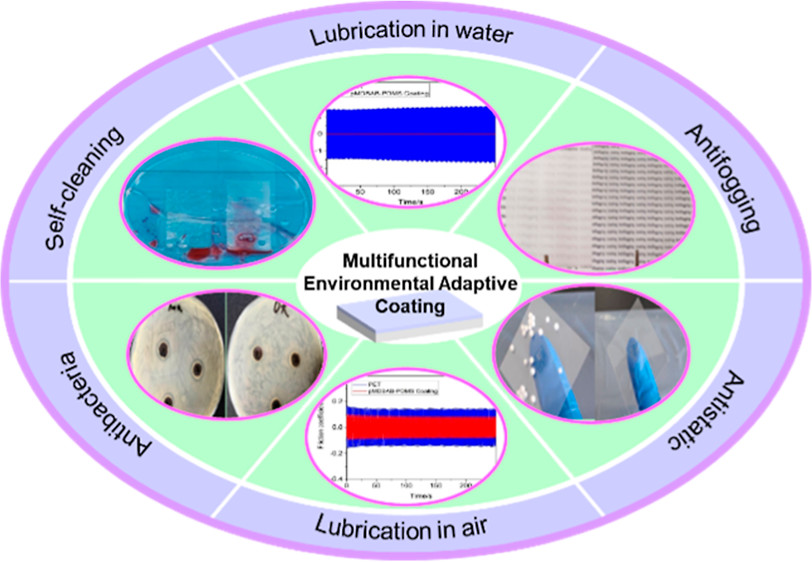
Multiple functional coating is urgently needed in complex service surroundings to meet various requirements. In this work, a brush-like amphiphilic copolymer of poly methacryloxyethyl dimethyl butyl ammonium bromide-polydimethylsiloxane (pMDBAB-PDMS) was synthesized to construct an environment-adaptive multifunctional coating based on the copolymer via the UV-curing method. The special molecule chains of the copolymer assembled predominately on the coating surface in different surroundings, which rendered the surface with various functions. In water-rich surroundings, the hydrophilic quaternary ammonium groups in the coating endow the coating surface with antifogging, oleophobicity underwater, self-cleaning, antibacteria, triboelectric resistance, and super lubrication properties. In dry air surroundings, the long, flexible, low surface energy molecular PDMS chains tend to distribute on the top of the coating surface, which gives a low friction coefficient and antioil properties. This work presents a strategy to construct environmental adaptive coating that has an important application prospect in the field of optical lens.
Keywords Plus:SURFACE FUNCTIONALIZATIONBLOCK-COPOLYMERSACRYLIC COATINGSFRICTIONCHEMISTRYSALT
Published in ACS APPLIED MATERIALS & INTERFACES,Volume14;10.1021/acsami.2c0182418901,PR 27 2022


