Abstract
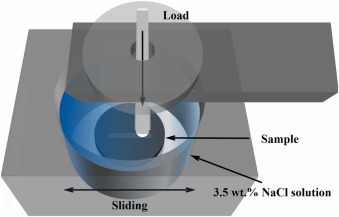
a-C:H films were produced on 316 L stainless steel via magnetron sputtering technique. The effects of bias voltage on the composition, structure and properties of the films were studied. The sp(2)C fraction grows as the bias voltage increases, and the internal stress and hardness increase constantly. In ambient air, the films deposited at - 150 V have the lowest friction coefficient (COF) of 0.095, while those at - 30 V have the lowest COF of 0.028 in salt solution, benefiting from the higher H content. The corrosion resistance of the film is affected comprehensively by the thickness, surface morphology, sp(2) clusters and transition layer. The a-C:H film at - 60 V has the lowest corrosion current density (5.41 x10(-11) A/cm(2)) and the highest protection efficiency (99.8 %).
Keywords Plus:DIAMOND-LIKE-CARBONTRIBOLOGICAL PROPERTIESDLC COATINGSELECTRONIC-PROPERTIESMAGNESIUM ALLOYTHIN-FILMSCORROSIONHYDROGENBEHAVIORPERFORMANCE
Published in TRIBOLOGY INTERNATIONAL,Volume175;10.1016/j.triboint.2022.107863,NOV 2022


