Abstract
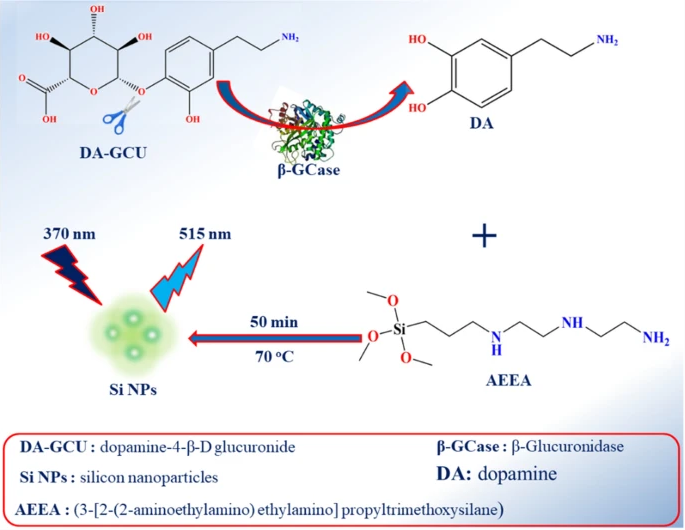
As a prodrug-converting enzyme, beta-glucuronidase (beta-GCase) is a lysosomal enzyme participating in the release of glucose from glucopyranosyl glycoside. In this work, for the first time, we have developed an analytical method exhibiting fluorometric signals for straightforward determination of beta-GCase using silicon nanoparticles (Si NPs). Via hydrothermal treatment, in the water bath of 70 degrees C for 50 min, dopamine (DA) reacts with (3-[2-(2-aminoethylamino) ethylamino] propyltrimethoxysilane) (AEEA) to produce green fluorescent Si NPs. Enlightened by such easy reaction and beta-GCase-triggered specific hydrolysis of dopamine-4-beta-D-glucuronide (DA-GCU) into DA, we have designed an analytical method for beta-GCase sensing through the production of Si NPs. Therefore, through the designed sensing platform, beta-GCase activity was monitored, and the limit of detection (LOD) for this study was 0.02 U/L. Furthermore, the feasibility of the method was assessed by measuring beta-GCase activity in human serum where recoveries and RSD were in the ranges 99-104% and 1.37-3.44, respectively.
Keywords Plus:FLUORESCENT-PROBELIVING CELLSWATER
Published in MICROCHIMICA ACTA,Volume189;10.1007/s00604-022-05528-7,NOV 2022


