Abstract
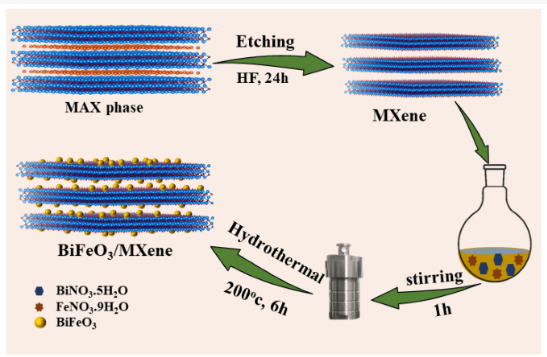
Developing a simple and efficient method for removing organic micropollutants from aqueous systems is crucial. The present study describes the preparation and application, for the first time, of novel MXene-decorated bismuth ferrite nanocomposites (BiFeO3/MXene) for the removal of six sulfonamides including sulfadiazine (SDZ), sulfathiazole (STZ), sulfamerazine (SMZ), sulfamethazine (SMTZ), sulfamethoxazole (SMXZ) and sulfisoxazole (SXZ). The properties of BiFeO3/MXene are enhanced by the presence of BiFeO3 nanoparticles, which provide a large surface area to facilitate the removal of sulfonamides. More importantly, BiFeO3/MXene composites demonstrated remarkable sulfonamide adsorption capabilities compared to pristine MXene, which is due to the synergistic effect between BiFeO3 and MXene. The kinetics and isotherm models of sulfonamide adsorption on BiFeO3/MXene are consistent with a pseudo-second-order kinetics and Langmuir model. BiFeO3/MXene had appreciable reusability after five adsorption-desorption cycles. Furthermore, BiFeO3/MXene is stable and retains its original properties upon desorption. The present work provides an effective method for eliminating sulfonamides from water by exploiting the excellent texture properties of BiFeO3/MXene.
Keywords Plus:ADSORPTIVE REMOVALCARBON NANOTUBESWATERANTIBIOTICSSTRATEGY
Published in molecules,Volume28;10.3390/molecules28041541,FEB 2023


