Abstract
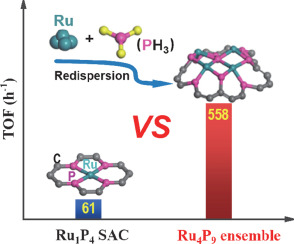
It is of great significance for upgrading single-atom catalysts (SACs) to further improve their intrinsic catalytic activities while maintaining the merits of maximum atom utilization and high selectivity. Here, we report a simple and practical strategy to construct phosphorus (P) atom bridged ruthenium (Ru) ensemble (Ru-P-Ru) in carbon skeleton, which is achieved by redispersing Ru clusters with C-P species and in-situ generated PH3. The turnover frequency of the Ru-P-Ru catalyst is 9-fold higher than that of the RuP4 SAC in the selective hydrodeoxygenation of o-phthalic anhydride, as well as other diverse hydrogenations of C=X bonds (X = O, C, N) with good recyclability. Experimental and computational studies reveal that the d-band centers of Ru in the Ru-P-Ru are closer to the Fermi level than that of isolated Ru SAC, significantly promoting the absorption and activation of substrates. This fabrication strategy is also applicable to other M-P-M catalysts, enriching the knowledge of atomically dispersed catalysts. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Keywords Plus:TOTAL-ENERGY CALCULATIONSFINDING SADDLE-POINTSSELECTIVE HYDROGENATIONPHTHALIC-ANHYDRIDELEVULINIC ACIDCATALYSTSPHOSPHORUSPERFORMANCEGRAPHENEDEHYDROGENATION
Published in CHINESE JOURNAL OF CATALYSIS,Volume45;10.1016/S1872-2067(22)64172-X,FEB 2023


