Abstract
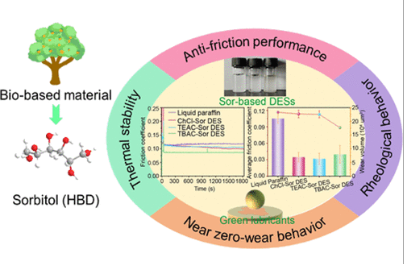
Deep eutectic solvents have emerged as promising alternatives to traditional lubricants due to their ease of preparation, low cost, low/no pollution, reproducibility, and unique antifriction and antiwear performance. Herein, green sorbitol-based deep eutectic solvents are successfully synthesized using d-sorbitol and quaternary ammonium salts as hydrogen bond donors and acceptors, respectively, through a simple heating and stirring method. The synthesized sorbitol-based deep eutectic solvents exhibit good thermostability, high viscosity, and favorable wettability on the steel surface. Notably, tribological tests demonstrated that the sorbitol-based deep eutectic solvents displayed outstanding antiwear and friction-reducing properties and were observed to achieve nearly wearless behavior on the steel surface under high contact pressure (2.16 GPa). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy revealed that complex tribofilms were formed because of the tribochemical reactions and physical adsorption of deep eutectic solvents on steel substrates, resulting in outstanding tribological properties. These results demonstrate that the as-synthesized sorbitol-based deep eutectic solvents are promising candidates for green and sustainable lubricating materials with eminent tribological properties. Furthermore, the present work may provide guidance and reference for the development of green and high-performance deep eutectic solvent-based lubricating materials.
Keywords Plus:TRIBOLOGICAL BEHAVIORLUBRICATIONRESISTANCEACIDTEMPERATUREDESIGNSYSTEM
Published in ACS SUSTAINABLE CHEMISTRY & ENGINEERING,Volume11,10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c05507;NOV 10 2023 

