Abstract
Light hydrocarbons are competitive novel energy sources and are expected to be alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. However, the leakage of unburned light hydrocarbon molecules in industrial applications would cause serious environmental problems, which limits future development and application of this novel energy source. Therefore, the removal of unburned light hydrocarbon molecules received extensive attention. The catalytic combustion technology is widely applied to their removal due to its economy, low energy consumption, high removal efficiency, mild reaction process and non-toxic and harmless product. This paper summarizes the research progress in catalytic combustion of light hydrocarbons over the past decade and its future challenges. It discusses systematically the different types of catalysts employed for catalytic combustion of light hydrocarbons in recent years and summarizes objectively their superiority and deficiency in catalytic applications. Subsequently, the reaction mechanism of catalytic combustion of light hydrocarbons and the characteristics of catalysts for different reaction mechanisms are discussed. Then, the structure-activity relationship of the catalysts for catalytic combustion of light hydrocarbons is concluded and discussed intensively. Finally, the prospect is presented for the rational design of efficient catalysts for catalytic combustion of light hydrocarbons, insight into the reaction mechanism and the development of characterization techniques.
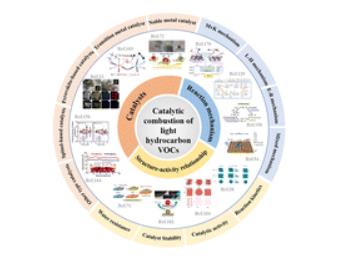
Various types of catalysts for the catalytic combustion of light hydrocarbon VOCs and their superiority and deficiency are described in detail. Meanwhile, their reaction mechanisms and structure-activity relationships are illustrated intensively.
Keywords Plus:HIGHLY-ACTIVE CATALYSTS;SPINEL COBALT OXIDES;METHANE COMBUSTION;LOW-TEMPERATURE;PROPANE COMBUSTION;PARTICLE-SIZE;LEAN METHANE;PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES;CO OXIDATION;PD
Published in JOURNAL OF MATERIALS CHEMISTRY A,Volume12;10.1039/d3ta07590g,MAR 26 2024


