Abstract
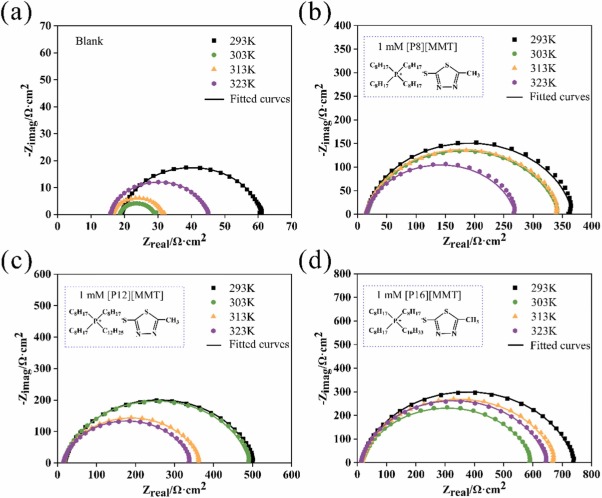
In this work, electrochemical experiments and friction tests were conducted to investigate anti-corrosion properties and lubrication performance of the 2-mercapto-5-methyl thiadiazole (MMT) based ILs as additives of ester oil. The outcomes of electrochemical experiments were further supported by quantum chemical simulation which clarified the reason for corrosion inhibition from a microscopic perspective. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy obtained from different temperatures (from 293 K to 323 K) showed that the inhibitors could reach a higher corrosion inhibition efficiency at 293 K. The experimental data exhibited that the adsorption behavior obeys Langmuir adsorption isotherm and the inhibitors adsorbed on the surface in a laying way seen from the results of theoretical simulation. Besides, SEM and XPS were employed to analyze the corrosion morphologies of immersion tests corroborating the presence of adsorption film on the steel surface. The tribological performance of MMT based ILs as base oil additives were examined by four-ball tester. The friction coefficient dropped by 47% and wear scar diameter decreased by 28% contrast to the base oil sample. The outstanding corrosion inhibition properties and friction-reducing and anti-wear performance could make it prospect for some industrial applications in energy saving.
Keywords Plus:MILD-STEEL,COPPER CORROSION,GREEN INHIBITOR,ACID,MECHANISM,DERIVATIVES,ADSORPTION,EXTRACT
Published in TRIBOLOGY INTERNATIONAL,Volume194;10.1016/j.triboint.2024.109473,JUN 2024


