Abstract
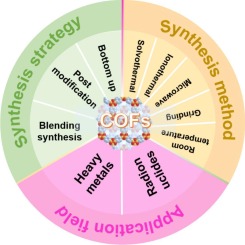
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are a novel type of porous materials, with unique properties, such as large specific surface areas, high porosity, pronounced crystallinity, tunable pore sizes, and easy functionalization, and thus have received considerable attention in recent years. COFs play an essential role in the catalytic degradation, adsorption, and separation of heavy metals, radionuclides. In recent years, considering several outstanding characteristics of COFs, including their good thermal/chemical stability, high crystallinity, and remarkable adsorption capacity, they have been widely used in the removal of various environment pollutants. This review primarily discusses the synthesis strategies of COFs along with their diverse synthesis methods, and provides a comprehensive summary and analysis of recent research advances in the use of COFs for removing heavy metal ions and radionuclides from water bodies. Additionally, the adsorption mechanism of COFs with regard to metal ions was determined by analyzing the structural characteristics of COFs. Finally, the future research directions on COFs adsorb rare earth element was discussed.
Keywords Plus:TRIAZINE-BASED FRAMEWORKS,INTERFACIAL POLYMERIZATION,SIMULTANEOUS REMOVAL,SELECTIVE REMOVAL,ROOM-TEMPERATURE,CRYSTALLINE,CARBON,EFFICIENT,CONSTRUCTION,PERFORMANCE
Published in SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT,Volume 939;10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173478,AUG 20 2024


