Abstract
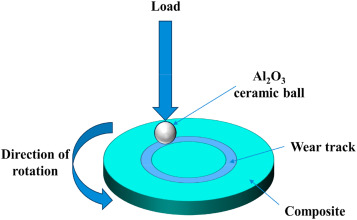
(NiCrW) 1-x (Al2O3) x composites with different nano-Al2O3 ratios (x = 0,1,2.5,5wt%) were prepared using powder metallurgy techniques. The influence of the Al2O3 content on the microstructure, phase composition, high -temperature mechanical properties, and wide -temperature -range friction and wear performance of the composites was investigated. The corresponding high -temperature strengthening and wear -resistance mechanisms were also investigated. The results indicated that as the alumina content increased, the tensile and compressive strengths of the composites decreased at room temperature (RT). However, at high temperatures (800 degrees C), the opposite trend was observed. Notably, the composite with 5wt % Al2O3 exhibits the highest tensile strength (189.20 MPa) and compressive strength (446.61 MPa) at 800 degrees C. The addition of alumina had a relatively minor impact on the friction coefficient of the composites but significantly affected the wear rate. Specifically, the composite with 5 wt % Al2O3 demonstrates optimal friction and wear performance at high temperatures. This enhancement was primarily attributed to the reinforcement of the mechanical properties of the matrix material owing to the addition of alumina. Additionally, the formation of a friction glaze layer rich in Cr2O3 and NiO oxides on the worn surface contributed to improved wear resistance. This study is important for understanding the performance and applications of metallic materials.
Keywords Plus:CRYSTAL-CHEMICAL APPROACH,TRIBOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS,LUBRICATING MATERIALS,WATER-VAPOR,ALLOY,DEFORMATION,ALUMINA,OXYGEN
Published in CERAMICS INTERNATIONAL,Volume 50;10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.05.276,SEP 1 2024


