Abstract
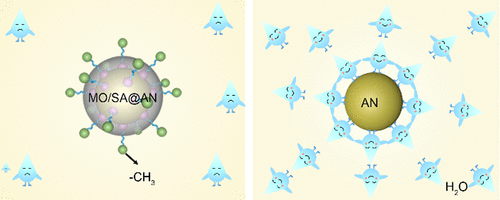
Ammonium nitrate (AN) is a very promising high-energy oxidant for use in solid propellants but suffers from serious hygroscopicity. While various coating materials (e.g., surfactants) have been employed to mitigate the hygroscopicity of AN, the interaction mechanisms between AN and these coatings remain inadequately understood. Here, we report the preparation of a mineral oil/stearic acid (MO/SA) hybrid coating that significantly reduces the hygroscopicity of AN. The hygroscopicity of AN is efficiently inhibited through interactions between the NH4 (+) of AN molecules and the -COOH of SA molecules, resulting in the formation of a dense and hydrophobic coating. Additionally, the defects in the SA coating are compensated for by the MO film. Consequently, MO/SA@AN particles with a low mass ratio of the coating (1.35 wt %) exhibit a low hygroscopicity of 7.24% after being kept in a 90% relative humidity environment at 20 degrees C for 24 h, representing a 48.10% decline of the hygroscopicity. Furthermore, MO/SA@AN maintains a high rate of hygroscopicity decline, at 29.5%, even at 35 degrees C and 90% RH after 24 h. Additionally, the hybrid coating effectively accelerates the thermal decomposition reactions of AN. This study provides valuable insights into the development of hybrid coatings with excellent antihygroscopic properties for AN.
Keywords Plus:SURFACE MODIFICATION,DECOMPOSITION,STABILIZATION,PHASEOXIDE
Published in LANGMUIR,Volume 40;10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c02497,JUL 23 2024


