Abstract
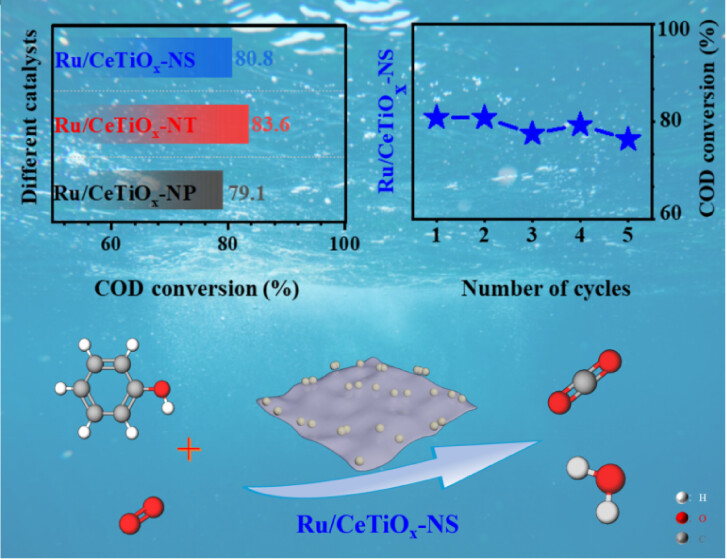
Phenol is one of the predominant hazardous organic compounds found in industrial wastewater. The use of catalytic oxidation technology to eliminate phenol has garnered significant interest due to its wide applicability and substantial economic benefits on an industrial scale. In this paper, CeTiOx supports with different morphology-supported Ru catalysts were tested in the CWAO of phenol and were characterized thoroughly using XRD, Raman, BET, NH3-TPD, H-2-TPR, HR-TEM, and XPS techniques. The results suggested that CeTiOx-NS and CeTiOx-NT exhibited superior performance in the oxidation of phenol compared to CeTiOx-NP due to their enhanced redox properties, higher surface acidity, and more active oxygen content. Ru/CeTiOx-NS, Ru/CeTiOx-NT, and Ru/CeTiOx-NP had comparable COD conversion rates with values of 80.8%, 83.6%, and 79.1%, respectively. However, ruthenium aggregation was observed on CeTiOx-NP, while Ru was well-dispersed on CeTiOx-NT. Additionally, stronger interaction between Ru and support was indicated by the pronounced hydrogen spillover during the reduction of Ru/CeTiOx-NT and Ru/CeTiOx-NS. Ru/CeTiOx-NS demonstrated the best catalytic stability, with only a 4.5% decrease in activity after five cycles. The resistance to carbon deposition and metal leaching of catalysts significantly influenced their stability, with carbon deposition identified as the primary factor impacting the catalyst stability.
Keywords Plus:TRICKLE-BED REACTOR,AIR OXIDATION,CE,CWAO,OXIDES,CO
Published in INDUSTRIAL & ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY RESEARCH;10.1021/acs.iecr.4c01515


