Abstract
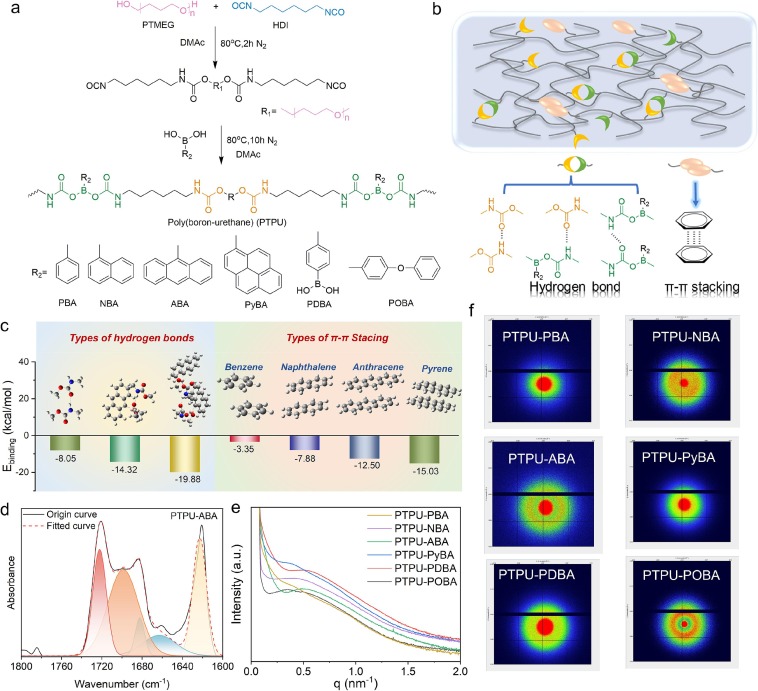
To enhance the mechanical properties of polyurethane elastomers, various strategies have been developed, including the incorporation of multiple hydrogen bonds, mechanical interlocking, and supramolecular interactions. However, achieving an optimal balance between strength and toughness while maintaining high tensile properties at both room and cryogenic temperatures remains a significant challenge. In this study, we synthesized a poly(boron-urethane) with ultra-high performance by introducing aromatic side chains into the polyurethane matrix. The resulting poly(boron-urethane) demonstrates remarkable mechanical properties, with tensile strength (70.1 +/- 4.4 MPa) and fracture toughness (437.5 +/- 61.1 MJ/m3). These exceptional mechanical properties were attributed to the synergistic effects of pi-pi stacking interactions and hierarchical hydrogen bonding. This synergy not only serves as reversible cross-linking points and sacrificial bonds that facilitate substantial energy dissipation, but also forms nanostructured domains that act as nanofillers, thereby enhancing the mechanical properties. Furthermore, the incorporation of bulky aromatic rings of the chain extenders mitigate the crystallization tendency of PTMEG, resulting in improved low-temperature flexibility. This chemcial modification contributes to significant tensile strength (100.6 MPa) and fracture toughness (237.5 MJ/m3) at -40 degrees C, along with excellent solvent resistance. Overall, the combination of pi-pi stacking and hierarchical hydrogen bonding, synergistically enhances the entropic elasticity of the elastomer network, effectively balancing the strength and toughness of the material across varying temperatures, making it well-suited for extremely cold environments.
Keywords Plus:SELF-HEALING POLYURETHANE,MECHANICAL-PROPERTIES,ROOM-TEMPERATURE
Published in CHEMICAL ENGINEERING JOURNAL,Volume 503;10.1016/j.cej.2024.158459,JAN 1 2025


