Abstract
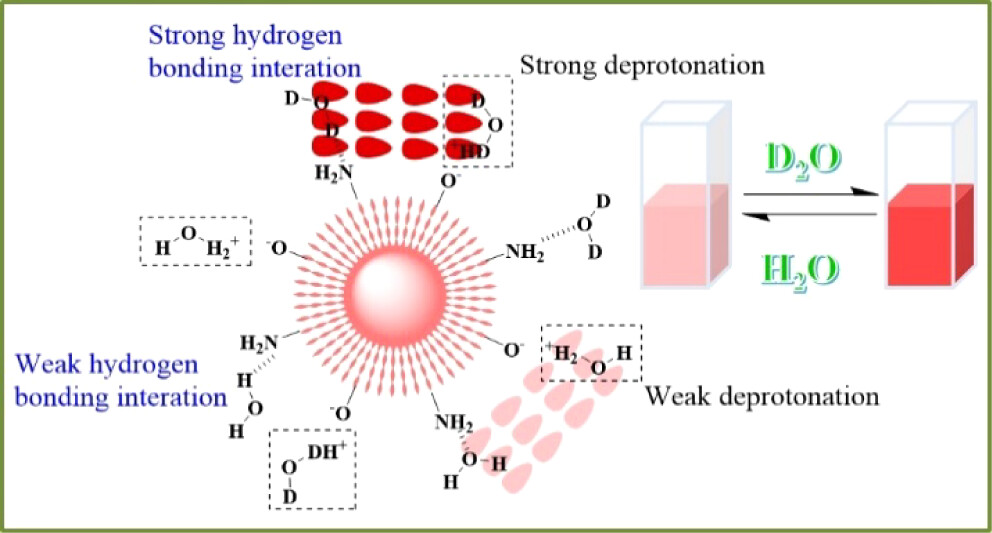
Distinguishing between D2O and H2O is crucial for the utilization of high-purity D2O in the nuclear industry, chemical analysis, biological pathway tracing, and other fields, as well as for ensuring the integrity of water quality and safeguarding human health, but challenging due to their highly analogous physical and chemical properties. On the basis of the fact that D2O exhibits superior hydrogen bond strength and deprotonation capacity for phenolic OH group compared to H2O, the red-emitting carbon dots (RCDs) with excellent optical properties, salt tolerance, photobleaching resistance, long-term storage stability, and biocompatibility were synthesized via a one-step strategy at room temperature. The RCDs demonstrated sensitivity for detecting D2O content in H2O and H2O content in D2O was found to be 0.060% and 0.15%, respectively. Collectively, this research expanded the potential applications of carbon nanomaterials and introduced a highly facile strategy for analyzing the isotopic purity of D2O.
Keywords Plus:WATER
Published in ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY,Volume97;10.1021/acs.analchem.5c00302,APR 2 2025


