Abstract
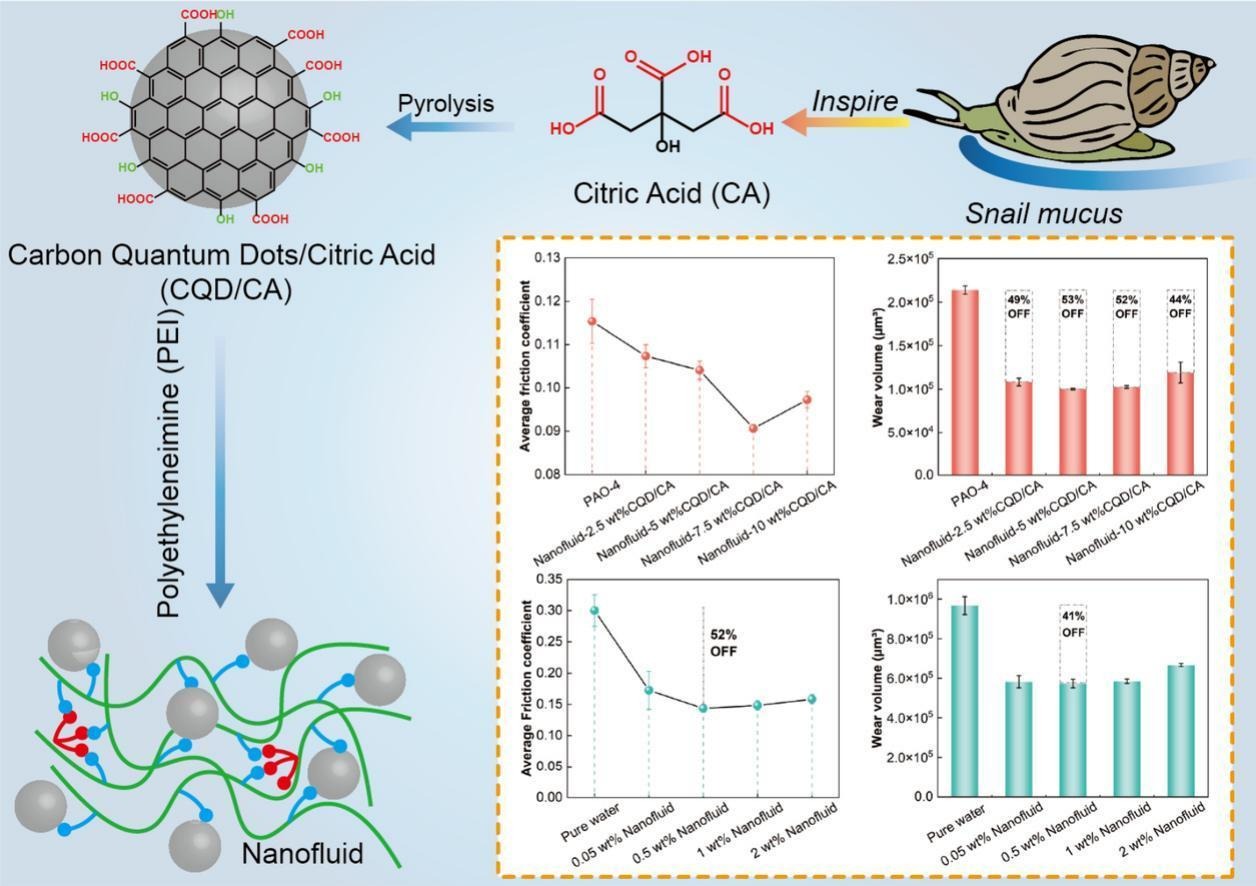
High-efficiency lubrication required by modern advanced industry cannot be met by single solid lubricant or liquid lubricant. The nanofluid combining the advantages of solid and liquid lubrication has become a very promising lubricating material. Here, inspired by the lubrication mechanism of snail mucus, a carbon quantum dots nanofluid is fabricated by a facile two-step synthesis. Firstly, carbon quantum dots (CQDs) are prepared by citric acid (CA) pyrolysis. Then, CQDs rich in carboxyl groups on the surface are used as crosslinking sites for polyethyleneimine, preparing high-performance nanofluid lubricants with three-dimensional and multiple adsorption networks. The nanofluids perform good fluidity under room temperature and excellent tribological behavior. The nanofluid containing 7.5 wt% CQD/CA shows a low friction coefficient of 0.091, and the wear decreases by 52% compared to PAO-4. This three-dimensional network structure endows the nanofluid with good load-bearing capacity, forming a tough lubricating film at the friction interface. The multiple adsorption from -NH2, -COOH, and -CONH- in nanofluids can effectively enhance the bonding force between the nanofluid and substrate, forming a stable lubricating film. Furthermore, CQDs can act as nanobearings, converting sliding friction into rolling friction. Additionally, the nanofluid can also serve as the water-based lubricant additive with excellent performance, thereinto the 0.5 wt% addition of nanofluid (7.5 wt% CQD/CA) reduces friction by 52% and wear by 41% compared to pure water.
Keywords Plus:LUBRICITY
Published in CHEMICAL ENGINEERING JOURNAL,Volume510;10.1016/j.cej.2025.161810,APR 15 2025


