Abstract
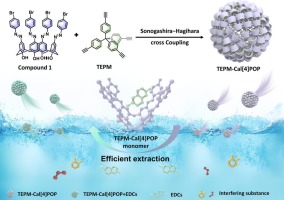
The detection of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) is imperative due to their inherent environmental persistence, bioaccumulation, and toxicity, which pose significant risks to both ecological systems and human health. Herein, a three-dimensional calix[4]arene porous organic polymer (named TEPM-Cal[4]POP) with hydrophobic cavity surface was developed through Sonogashira-Hagihara cross coupling utilizing tetrakis-(4ethynylphenyl)methane (TEPM) as bridging unit. The TEPM-Cal[4]POP displayed excellent extraction capacity for EDCs (diethylstilbestrol, estrone, norgestre and norethindrone acetate) on account of introducing of electronrich cavity. The extraction mechanism was further explored by adsorption thermodynamic, adsorption kinetics and theoretical calculation including density functional theory (DFT) calculation, reduced density gradient (RDG) and electrostatic potential (ESP) analyses. Thus, analytical methods of EDCs based on TEPM-Cal[4]POP as solid phase extractant were established coupled with high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet (HPLC-UV). The low limits of detection (LODs) were 0.38, 0.41, 0.55, 0.56 mu g/L, respectively in the linear response of 0.5 to 4000 mu g/L, respectively. The method recoveries were 88.4-102 % with the RSD of 0.518-9.93 %. These results suggested that the proposed method can be served as a good alternative analytical method applied in sensitive detection of EDCs in milk, pork and seafish samples.
Keywords Plus:SOLID-PHASE EXTRACTION,NANOPARTICLES,REMOVAL
Published in CHEMICAL ENGINEERING JOURNAL,Volume518;10.1016/j.cej.2025.164858,AUG 15 2025


